Navigating the stock market is a thrilling, yet often turbulent, journey. While the potential for hefty returns is enticing, it’s crucial to remember that market volatility is an inherent part of the game. Shielding your portfolio from the unpredictable tides of the stock market is paramount to safeguarding your investments and achieving your financial goals. This is where the art of risk management comes into play.
Effective risk management strategies are not about avoiding risk altogether – they are about understanding, assessing, and mitigating it. This article dives into the essential techniques that seasoned investors employ to navigate market uncertainty and preserve their portfolio’s value. From diversification and asset allocation to understanding market cycles and employing stop-loss orders, we’ll explore the tools and techniques that can help you master the art of stock market risk management and achieve sustainable investment success.
Understanding Different Types of Market Risk
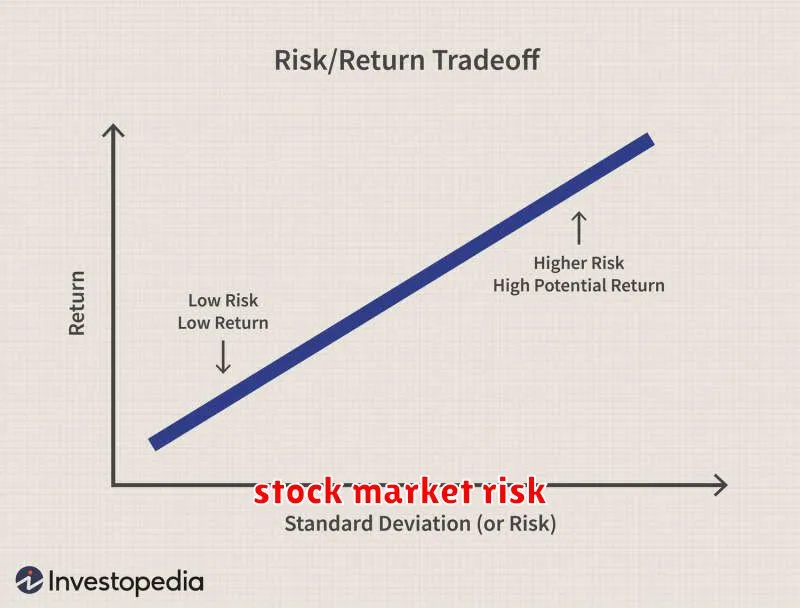
Navigating the stock market is a journey filled with opportunities and potential pitfalls. While the prospect of substantial returns is enticing, it’s crucial to acknowledge and manage the inherent risks. Market risk, an umbrella term encompassing various threats, can significantly impact your investment portfolio. Understanding the different types of market risk is the first step towards informed decision-making and mitigating potential losses.
Market risk, also known as systematic risk, refers to the uncertainty inherent in the overall market. This risk can be influenced by a multitude of factors, including economic conditions, political events, and investor sentiment.
Here are some of the most prevalent types of market risk:
- Interest rate risk: This risk stems from changes in interest rates, affecting the value of bonds and other fixed-income securities. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds falls, as investors can purchase new bonds with higher interest payments.
- Inflation risk: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money. If inflation rises faster than the return on your investments, your real return may be diminished.
- Currency risk: Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the value of investments held in foreign currencies. If the value of your investment currency weakens relative to the currency you need to convert it to, your returns can be negatively affected.
- Volatility risk: Market volatility refers to the degree of price fluctuations in a specific stock, index, or market. High volatility can create sudden and significant swings in investment values, making it challenging to predict short-term movements.
While market risk cannot be entirely eliminated, understanding its various forms empowers investors to develop strategies for mitigating its impact. By acknowledging the inherent uncertainties and taking proactive steps to manage risk, you can navigate the stock market with greater confidence and strive towards achieving your investment goals.
Diversification: Don’t Put All Your Eggs in One Basket
The old adage, “Don’t put all your eggs in one basket,” holds true in the realm of investing. Diversification is a fundamental principle of sound risk management, and it’s crucial for protecting your portfolio from market fluctuations. By spreading your investments across various asset classes, industries, and geographies, you reduce the impact of any single investment’s performance on your overall portfolio.
Imagine you have all your eggs in one basket, and that basket falls. You lose everything. But, if you have your eggs in multiple baskets, the loss of one basket won’t wipe out your entire egg collection. Similarly, in investing, diversifying your portfolio helps mitigate the risk of significant losses if one particular investment performs poorly.
Diversification comes in many forms. You can diversify by:
- Asset classes: Investing in stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and cash.
- Industries: Investing in companies from different sectors, such as technology, healthcare, and energy.
- Geographies: Investing in companies from different countries to benefit from global growth opportunities.
By following a well-thought-out diversification strategy, you can build a portfolio that’s more resilient to market volatility and better positioned for long-term growth. Remember, diversification is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. Regularly review and adjust your portfolio to ensure it aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Setting Realistic Investment Goals and Time Horizon
Before diving into complex risk management strategies, the foundation of any successful investment strategy lies in establishing realistic goals and understanding your time horizon. This crucial step provides a clear roadmap for your investment journey, allowing you to make informed decisions and stay on track.
Start by defining your financial goals. Are you saving for retirement, a down payment on a house, or a child’s education? Identifying these objectives will determine the type of investments you pursue and the level of risk you’re comfortable taking.
Once you’ve outlined your goals, consider your time horizon. This refers to the duration you intend to hold your investments. A longer time horizon allows for greater potential growth but also necessitates a higher risk tolerance, as market fluctuations can be absorbed over time. Conversely, a shorter time horizon requires a more conservative approach with lower-risk investments to protect your capital.
The key is to align your goals with your time horizon. If you’re saving for retirement decades away, you can afford to take on more risk with investments like stocks. However, if you’re saving for a down payment within a few years, a more conservative approach with bonds or fixed-income investments may be preferable.
Establishing realistic goals and understanding your time horizon provides a solid foundation for your investment journey. It empowers you to choose investments aligned with your risk tolerance and financial objectives, fostering a clear path toward achieving your financial aspirations.
Determining Your Risk Tolerance and Capacity
Understanding your risk tolerance and capacity is crucial for effective portfolio management. Risk tolerance reflects your emotional ability to stomach potential losses, while risk capacity signifies your financial ability to withstand market fluctuations.
To assess your risk tolerance, consider your investment goals, time horizon, and comfort level with potential losses. If you have a long-term perspective and can handle volatility, you may be more comfortable with riskier assets. Conversely, if you’re nearing retirement or have a short-term horizon, you may prefer a more conservative approach.
Risk capacity depends on your financial situation, including your income, savings, and outstanding debts. A strong financial foundation allows you to weather market downturns without compromising your financial security.
By understanding your risk tolerance and capacity, you can create a portfolio that aligns with your needs and goals. A well-structured investment plan helps you manage risk effectively and pursue long-term financial success.
Importance of Asset Allocation Strategies
In the dynamic realm of the stock market, where volatility reigns supreme, crafting a robust investment strategy is paramount. Among the arsenal of risk management tools at an investor’s disposal, asset allocation emerges as a cornerstone, playing a pivotal role in shielding portfolios from the unpredictable tides of the market.
At its core, asset allocation involves strategically distributing investment capital across various asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. The rationale behind this approach is rooted in the principle of diversification, a fundamental tenet of investing that aims to mitigate risk by spreading investments across different assets with varying levels of risk and return potential.
A well-crafted asset allocation strategy acts as a buffer against market fluctuations. By diversifying across different asset classes, investors can reduce their exposure to any single asset’s price movements. If one asset class experiences a downturn, the overall portfolio can be cushioned by the positive performance of other assets. This diversification effect helps to stabilize returns and minimize losses during market corrections or downturns.
Furthermore, asset allocation allows investors to align their portfolio with their risk tolerance and investment goals. Individuals with a higher risk appetite may allocate a larger portion of their assets to stocks, which historically have the potential for higher returns but also carry greater volatility. Conversely, investors seeking more conservative investments may prioritize bonds, which typically offer lower returns but provide greater stability.
In conclusion, asset allocation is a crucial aspect of any sound investment strategy. By diversifying across different asset classes, investors can reduce risk, enhance portfolio stability, and achieve their financial goals more effectively. It is a cornerstone of risk management that empowers investors to navigate the complexities of the stock market with greater confidence and resilience.
Stop-Loss Orders: Limiting Potential Losses
In the dynamic world of stock market investing, risk management is paramount. While the allure of profits is undeniable, it’s equally crucial to safeguard your portfolio from potential losses. Stop-loss orders are a valuable tool in your risk management arsenal, designed to automatically sell your stock when it reaches a predetermined price, limiting potential losses.
Imagine you’ve invested in a stock that starts to decline unexpectedly. A stop-loss order acts like a safety net, automatically triggering a sale of your stock when its price reaches a specific threshold you’ve set. This prevents further erosion of your investment by cutting your losses at a defined point.
The effectiveness of stop-loss orders lies in their ability to execute trades swiftly and objectively. They eliminate the emotional factor that can often hinder rational decision-making in times of market volatility. By pre-setting a trigger price, you’re essentially automating the decision to sell, ensuring a more disciplined approach to managing risk.
However, it’s essential to understand that stop-loss orders aren’t a foolproof solution. They can be subject to slippage, which occurs when the market price dips below your stop-loss price before your order can be executed. Additionally, they might not be suitable for every investment strategy, particularly those focused on long-term growth with the expectation of high volatility.
When employing stop-loss orders, consider these key factors:
- Set realistic stop-loss prices: Don’t place your stop-loss too close to the current price, as it could trigger a sale on minor fluctuations.
- Consider market volatility: Adjust your stop-loss price based on the historical volatility of the specific stock or market sector.
- Monitor and adjust: Regularly review your stop-loss orders and adjust them as needed based on market conditions and your investment goals.
In conclusion, stop-loss orders offer a valuable strategy for limiting potential losses in your stock portfolio. By implementing them with a thoughtful and disciplined approach, you can enhance your risk management practices and protect your hard-earned investments. Remember, a well-managed portfolio is a key ingredient in achieving your financial goals.
Hedging Strategies for Downside Protection
In the dynamic world of stock markets, risk management is paramount. While aiming for growth, safeguarding your portfolio against potential losses is equally crucial. Hedging strategies play a pivotal role in achieving this balance, offering a safety net against market downturns.
Hedging involves taking positions that offset potential losses in your core investments. It’s like having an insurance policy for your portfolio. Here are some common hedging strategies:
1. Short Selling
Short selling involves borrowing shares of a stock and immediately selling them in the market. The hope is to buy back the shares at a lower price later, pocketing the difference. This strategy is a direct bet against the stock’s price. However, it carries significant risks, including potential unlimited losses if the stock price rises.
2. Put Options
Put options give you the right, but not the obligation, to sell a stock at a specific price (strike price) by a certain date (expiration date). If the stock price falls below the strike price, you can exercise the option to sell it at a higher price, protecting against losses. Put options are a relatively common and flexible hedging tool.
3. Diversification
While not a traditional hedging strategy, diversification is a cornerstone of risk management. By investing in a variety of assets across different sectors and asset classes, you reduce the impact of any single investment’s performance on your overall portfolio. This approach helps mitigate losses and smooth out returns over time.
Hedging strategies are not foolproof and should be carefully considered. They come with their own costs and risks. It’s essential to understand the nuances of each strategy and its potential impact on your portfolio before implementing it. Consulting with a financial advisor is always recommended to tailor a suitable hedging strategy for your specific risk tolerance and investment objectives.
Position Sizing and Managing Portfolio Volatility
Position sizing is a crucial aspect of risk management that involves determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each investment. It plays a vital role in managing portfolio volatility, which refers to the fluctuations in the value of your investments over time. By carefully determining the size of your positions, you can mitigate potential losses and protect your overall portfolio.
A key principle of position sizing is to avoid overexposure to any single investment. Diversifying your portfolio across different asset classes and sectors helps to spread risk and reduce the impact of any individual investment’s performance on your overall returns. However, even within a diversified portfolio, it’s essential to manage the size of individual positions.
One common approach to position sizing is to use a percentage-based allocation strategy. This involves allocating a specific percentage of your portfolio to each investment. For example, you might decide to allocate 10% of your portfolio to a particular stock or 5% to a specific bond fund. The percentage allocation can be adjusted based on your risk tolerance, investment goals, and the expected volatility of the investment.
Another strategy is to use risk-based position sizing. This approach considers the volatility of each investment and allocates capital accordingly. Higher-volatility investments, which tend to fluctuate more in price, should be allocated a smaller percentage of your portfolio than lower-volatility investments. By adjusting your position sizes based on risk, you can help to reduce overall portfolio volatility.
Managing portfolio volatility is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adjustments. It’s essential to regularly review your investment holdings and make necessary changes to your position sizes based on market conditions, your risk tolerance, and your investment goals. By taking a disciplined approach to position sizing and volatility management, you can enhance the resilience of your portfolio and increase your chances of achieving your long-term investment objectives.
Regular Portfolio Rebalancing and Adjustments
Regular portfolio rebalancing and adjustments are essential components of a sound risk management strategy. Rebalancing involves adjusting your asset allocation to maintain your desired risk profile and ensure your portfolio aligns with your investment goals. This process involves selling some assets that have performed well and buying those that have underperformed, bringing your portfolio back to its initial target allocation.
The frequency of rebalancing depends on your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and market conditions. Generally, rebalancing annually or semi-annually is a good starting point. However, if you have a high risk tolerance and are investing for the long term, you may choose to rebalance less frequently. Conversely, if you have a low risk tolerance and are approaching retirement, you may need to rebalance more frequently.
Benefits of Regular Rebalancing:
- Reduces risk: By selling assets that have appreciated and buying assets that have depreciated, rebalancing helps to reduce the overall risk of your portfolio.
- Improves returns: Rebalancing can improve your long-term returns by taking advantage of market fluctuations and ensuring that you are not overexposed to any particular asset class.
- Maintains discipline: It encourages you to stick to your investment plan and avoid emotional decisions that can lead to poor investment outcomes.
Tips for Effective Rebalancing:
- Define your risk tolerance and investment goals clearly: This will help you determine your desired asset allocation and rebalancing schedule.
- Choose a rebalancing strategy and stick to it: Consistency is key to successful rebalancing.
- Use a disciplined approach: Don’t let market fluctuations dictate your rebalancing decisions.
Regular portfolio rebalancing is an essential strategy for managing risk and maximizing returns. By staying disciplined and following a consistent approach, you can ensure that your portfolio stays aligned with your investment goals and helps you achieve your financial objectives.
The Role of Research and Due Diligence
In the dynamic realm of the stock market, where fortunes can be made and lost with equal ease, research and due diligence stand as the cornerstones of a sound risk management strategy. Before committing capital to any investment, a thorough understanding of the underlying company, its industry, and market conditions is paramount. By conducting comprehensive research, investors can gain valuable insights into the potential risks and rewards associated with a particular stock.
Research encompasses a wide range of activities, including:
- Analyzing the company’s financial statements to assess its profitability, debt levels, and cash flow
- Evaluating the company’s management team, its track record, and its strategic direction
- Understanding the competitive landscape of the industry in which the company operates
- Examining macroeconomic trends and their potential impact on the company’s performance
Due diligence goes beyond mere research. It involves a more in-depth examination of the company, including:
- Independent verification of financial data and other information provided by the company
- Assessment of the company’s legal and regulatory environment
- Evaluation of the company’s operational risks, such as supply chain disruptions or environmental concerns
- Reviewing the company’s corporate governance practices and its commitment to ethical behavior
By undertaking thorough research and due diligence, investors can:
- Identify potential red flags and avoid investments with high risk profiles
- Gain a better understanding of the company’s strengths and weaknesses
- Make more informed investment decisions based on a solid foundation of knowledge
- Enhance their ability to navigate market volatility and protect their portfolio from unexpected losses
In conclusion, research and due diligence are essential components of a robust risk management strategy. By diligently scrutinizing potential investments, investors can mitigate their exposure to avoidable risks and position themselves for greater success in the stock market.
Emotional Discipline in Investing
Investing is a journey, not a sprint. It requires a long-term perspective and the ability to navigate the inevitable ups and downs of the market. While financial knowledge is crucial, emotional discipline plays an equally important role in achieving your investment goals.
Emotional investing, driven by fear and greed, can lead to impulsive decisions that hurt your portfolio. When markets are soaring, it’s easy to get caught up in the hype and chase after “hot” stocks. Conversely, when the market dips, fear can paralyze you, leading to panic selling. These emotional reactions often result in buying high and selling low, the antithesis of a successful investment strategy.
Mastering emotional discipline requires developing a calm and rational approach to investing. It’s about understanding your risk tolerance, sticking to your investment plan, and resisting the urge to react to short-term market fluctuations. Here are a few tips:
- Define Your Investment Goals: Clearly articulate your financial objectives and create a well-defined investment plan. This will provide a roadmap and serve as a guiding principle when market conditions become volatile.
- Embrace Diversification: Spreading your investments across different asset classes and sectors can help mitigate risk and reduce volatility.
- Adopt a Long-Term Perspective: Remember that investing is a marathon, not a sprint. Avoid short-term speculation and focus on building wealth over the long term.
- Practice Patience: Market fluctuations are inevitable, and it’s important to remain patient and avoid impulsive decisions. Resist the urge to time the market and stay invested through both bull and bear markets.
- Seek Professional Guidance: If you’re struggling with emotional investing, consider consulting a financial advisor who can provide objective advice and help you maintain a disciplined approach.
Ultimately, emotional discipline is a key ingredient in successful investing. By understanding your emotions and cultivating a rational approach, you can shield your portfolio from the pitfalls of emotional investing and navigate the market with confidence.
Avoiding Common Investment Mistakes
Navigating the stock market can be an exciting and potentially lucrative endeavor, but it’s also fraught with risks. While you can’t eliminate all risks, there are common pitfalls to avoid that can significantly impact your portfolio’s performance. By understanding these mistakes and taking steps to mitigate them, you can enhance your chances of achieving your investment goals.
One of the most prevalent errors is emotional investing. When markets are booming, it’s easy to get swept up in the euphoria and overextend your investments, chasing high returns. Conversely, during market downturns, fear can lead to panic selling, locking in losses. This emotional rollercoaster can lead to poor decision-making.
Another common mistake is lack of diversification. Putting all your eggs in one basket, so to speak, exposes you to excessive risk. A diversified portfolio, spread across different asset classes, industries, and geographical regions, helps mitigate the impact of any single investment’s poor performance.
Ignoring fundamentals is another pitfall. Many investors get caught up in hype and trends, investing in companies without understanding their financial health, business model, or management team. It’s crucial to perform thorough research and analyze a company’s fundamentals before investing.
Failing to rebalance your portfolio is another mistake. Over time, the asset allocation you initially chose may shift due to market fluctuations. Regularly rebalancing ensures that your portfolio remains aligned with your risk tolerance and investment goals.
Finally, not having a clear investment plan can lead to confusion and impulsive decisions. Having a well-defined investment strategy, including your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon, provides a roadmap for navigating market volatility.
By avoiding these common mistakes and employing sound risk management strategies, you can increase your odds of achieving long-term investment success. Remember, patience, discipline, and a long-term perspective are key to weathering market fluctuations and maximizing your portfolio’s potential.
Tax Implications of Stock Market Investments
Investing in the stock market can be a rewarding way to grow your wealth, but it’s crucial to understand the tax implications involved. The tax treatment of your stock market investments can significantly impact your overall returns. This section will provide an overview of the key tax considerations associated with stock market investments.
Capital Gains Tax
One of the primary tax implications of stock market investments is capital gains tax. This tax is levied on the profit you realize when you sell a stock or other investment for more than you paid for it. Capital gains are classified as either short-term or long-term, depending on how long you held the investment.
- Short-term capital gains: These gains are realized on investments held for less than one year and are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate.
- Long-term capital gains: These gains are realized on investments held for more than one year and are taxed at preferential rates, which vary depending on your income bracket.
Dividends
Dividends are payments made by companies to their shareholders, representing a portion of the company’s profits. Dividends are also subject to taxation, and the tax rate depends on the type of dividend and your income level.
- Qualified dividends: These dividends are taxed at preferential rates, similar to long-term capital gains.
- Unqualified dividends: These dividends are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate.
Tax-Loss Harvesting
Tax-loss harvesting is a strategy that allows investors to offset capital gains with capital losses. This can reduce your overall tax liability. If you sell a stock at a loss, you can deduct that loss from any capital gains you realize, potentially reducing your tax bill. However, it’s important to note that there are rules surrounding wash sales, which prevent you from immediately repurchasing the same or substantially similar security.
Tax-Advantaged Accounts
Investing in tax-advantaged accounts, such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) and 401(k)s, can provide significant tax benefits. These accounts allow you to grow your investments tax-deferred, meaning you won’t have to pay taxes on the earnings until you withdraw the money in retirement.
Understanding the tax implications of stock market investments is essential for maximizing your returns and minimizing your tax burden. By staying informed about the different tax rules and strategies, you can make informed decisions about your investments and ensure that you’re taking full advantage of the tax benefits available to you.
Seeking Professional Financial Advice
Navigating the stock market can be a complex and often daunting task. While there are many resources available to help investors, seeking professional financial advice can be invaluable for shielding your portfolio from unnecessary risk.
A financial advisor brings expertise and objectivity to your investment decisions. They can provide a personalized assessment of your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. This allows them to create a tailored investment strategy that aligns with your individual needs and aspirations.
Here are some key reasons why seeking professional financial advice can be beneficial:
- Expert Guidance: Financial advisors possess in-depth knowledge of the market, investment vehicles, and strategies. They can help you navigate market fluctuations and make informed decisions based on your specific circumstances.
- Risk Management: A financial advisor can help you develop a comprehensive risk management strategy to protect your portfolio from potential losses. They can guide you on diversification, asset allocation, and other strategies to mitigate downside risks.
- Objectivity: Emotional biases can cloud our judgment when it comes to investments. A financial advisor provides an objective perspective, helping you avoid impulsive decisions and stick to your long-term financial plan.
- Financial Planning: Financial advisors can assist with broader financial planning needs, such as retirement planning, college savings, and estate planning. They can help you create a holistic financial roadmap for the future.
Ultimately, the decision to seek professional financial advice is a personal one. If you are unsure about how to manage your investments, or if you feel overwhelmed by the complexities of the stock market, consulting with a qualified financial advisor can provide the peace of mind and guidance you need to secure your financial future.
Building a Resilient Portfolio for the Long Term
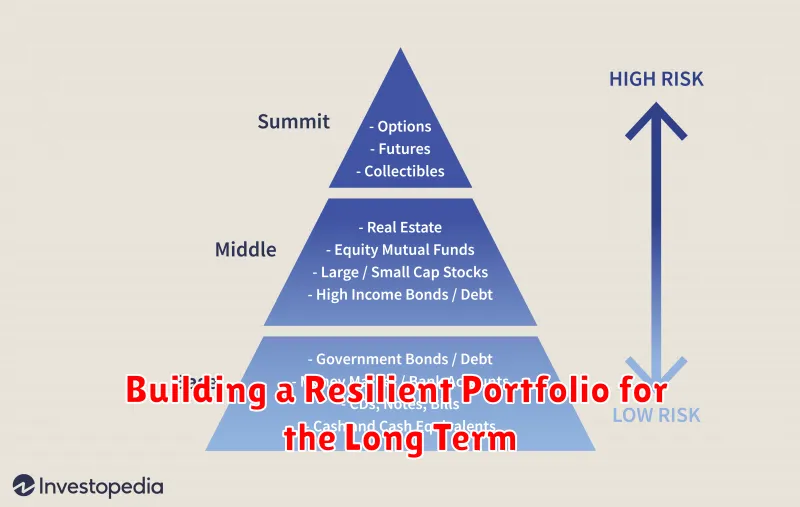
In the dynamic realm of investing, building a resilient portfolio is paramount for achieving long-term financial success. A resilient portfolio can weather market storms and emerge stronger, enabling you to stay invested through market cycles and reap the rewards of compound growth. This article delves into practical strategies for mastering stock market risk management and constructing a portfolio that can withstand volatility and deliver enduring returns.
Diversification lies at the heart of portfolio resilience. Spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographies helps mitigate the impact of any single investment’s performance. A well-diversified portfolio includes stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and other assets, reducing overall portfolio risk. Consider a global perspective, investing in international markets to access opportunities beyond your domestic economy.
Asset Allocation is a crucial aspect of risk management. By determining the proportion of your portfolio allocated to different asset classes, you can adjust your risk exposure based on your investment goals and time horizon. A strategic asset allocation strategy involves balancing risk and return, ensuring your portfolio aligns with your individual needs and risk tolerance.
Rebalancing is an essential practice for maintaining a resilient portfolio. Over time, asset prices fluctuate, leading to changes in your portfolio’s initial allocation. Rebalancing involves adjusting your asset allocation back to your desired proportions periodically, ensuring you don’t become overly exposed to any single asset class or sector.
Dollar-Cost Averaging is a powerful strategy for mitigating market volatility. This approach involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions. By buying both high and low, dollar-cost averaging helps reduce the average cost of your investments over time and minimize the impact of short-term market fluctuations.
Long-Term Perspective is fundamental to building a resilient portfolio. Investing is a marathon, not a sprint. Avoid impulsive decisions driven by short-term market noise, and remain focused on your long-term goals. Embrace the power of compound growth, allowing your investments to work for you over time.
By implementing these risk management strategies, you can build a portfolio that not only survives but thrives during market turbulence. Embrace diversification, asset allocation, rebalancing, dollar-cost averaging, and a long-term perspective to cultivate a resilient portfolio that stands the test of time.