Navigating the commodity market can be a daunting task, especially for new investors. The landscape is vast and dynamic, encompassing everything from precious metals like gold and silver to energy resources like oil and natural gas. With so many factors influencing prices, from global supply and demand to geopolitical events, it can feel overwhelming to grasp the intricacies of this market. But fear not, for this comprehensive guide is designed to provide you with the essential knowledge you need to confidently explore the world of commodities and make informed investment decisions.
Whether you’re a seasoned investor seeking to diversify your portfolio or a newcomer eager to learn about this exciting asset class, this article will delve into the various facets of the commodity market. We’ll explore the key factors that drive price fluctuations, discuss different types of commodities, and provide insights into potential investment opportunities. By the end of this journey, you’ll have a solid understanding of the commodity market and be equipped to make informed decisions that align with your financial goals.
What are Commodities and How are They Traded?
Commodities are basic goods that serve as raw materials or have intrinsic value. They are typically traded in large quantities and are often used in manufacturing, energy production, and other industries. Examples of commodities include oil, gold, wheat, and copper.
Commodities are traded on exchanges, which are marketplaces where buyers and sellers meet to trade. The most common types of commodity exchanges are futures exchanges, where contracts for future delivery of a commodity are traded. Futures contracts allow buyers and sellers to lock in a price for a commodity at a future date, regardless of the spot price at that time.
Commodities are typically traded in the following ways:
- Futures contracts: These contracts oblige the buyer to purchase and the seller to deliver a specific quantity of a commodity at a specific future date and price.
- Spot contracts: These contracts are for the immediate delivery of a commodity at the prevailing market price.
- Options contracts: These contracts give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a commodity at a specific price on or before a certain date.
Different Categories of Commodities
Commodities are raw materials that are traded in bulk. They can be classified into several categories, each with its unique characteristics, uses, and investment implications.
Energy
Energy commodities are the most familiar category, encompassing fuels like crude oil, natural gas, and refined petroleum products. These commodities are crucial for transportation, power generation, and industrial processes. Their prices are influenced by factors such as global demand, geopolitical events, and technological advancements in alternative energy sources.
Metals
Metals are another prominent commodity category, encompassing both precious metals like gold and silver, and industrial metals like copper, aluminum, and iron ore. Precious metals are often viewed as safe haven assets during economic uncertainty, while industrial metals are vital for manufacturing and construction.
Agricultural Products
Agricultural commodities encompass a wide array of products, including grains (e.g., wheat, corn, rice), oilseeds (e.g., soybeans, rapeseed), livestock (e.g., cattle, hogs), and coffee, sugar, and cotton. These commodities are essential for food production, and their prices are influenced by weather patterns, global food demand, and government policies.
Other Commodities
Beyond the major categories, there are a diverse range of other commodities. These include rubber, cocoa, timber, and livestock. Their prices are driven by specific factors related to their respective uses and production processes.
Understanding these different categories of commodities is crucial for investors seeking to diversify their portfolios and capitalize on the opportunities and risks presented by this vast and dynamic market.
Factors Driving Commodity Prices
The prices of commodities, which are raw materials like oil, gold, and wheat, are influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the volatile commodity markets.
Supply and demand is the cornerstone of commodity price determination. When demand for a commodity exceeds supply, prices tend to rise. Conversely, when supply outpaces demand, prices decline.
Economic growth plays a significant role. Strong economic growth often translates to increased demand for commodities, driving prices upward. Conversely, economic downturns can lead to reduced demand and lower prices.
Geopolitical events can have a profound impact. Wars, political instability, and trade disputes can disrupt supply chains, leading to price volatility. For instance, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine has significantly impacted global wheat prices.
Technological advancements can influence commodity prices in various ways. New technologies can lead to increased efficiency in extraction or production, potentially increasing supply and lowering prices. On the other hand, some technologies may create new demand for certain commodities.
Financial markets also contribute to commodity price movements. Speculation and hedging activities by investors and financial institutions can influence prices, sometimes leading to significant fluctuations.
Government policies, such as subsidies, tariffs, and environmental regulations, can impact commodity markets. Policies that encourage production can lead to increased supply and lower prices. Conversely, policies that restrict production or impose taxes can drive prices upward.
In conclusion, understanding the interplay of these factors is essential for making informed investment decisions in the commodity markets. Investors should stay informed about current events, economic trends, and policy developments that could affect commodity prices.
Understanding Supply and Demand Dynamics
The fundamental principle driving commodity prices is the interplay of supply and demand. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the volatile world of commodity markets.
Supply refers to the amount of a commodity available in the market. Factors influencing supply include production costs, technological advancements, weather conditions, and government policies. For example, a drought could significantly impact the supply of agricultural commodities like wheat and corn.
Demand, on the other hand, represents the quantity of a commodity that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price. Factors driving demand include economic growth, consumer preferences, and the availability of substitutes. A booming economy could lead to increased demand for industrial metals like copper and aluminum.
The relationship between supply and demand is inversely proportional. When supply exceeds demand, prices tend to fall. Conversely, when demand outstrips supply, prices rise. This basic principle is reflected in the supply and demand curve, a visual representation of this relationship.
Understanding how supply and demand dynamics influence commodity prices is essential for investors. By closely monitoring these factors, investors can identify potential opportunities and mitigate risks in the commodity markets.
The Role of Geopolitics in Commodity Markets
The global commodity market is a complex web of supply and demand, influenced by a myriad of factors. Among these factors, geopolitics plays a pivotal role, shaping market dynamics and influencing prices. Geopolitical events, from political instability to international trade wars, can significantly impact the production, transportation, and consumption of commodities, leading to price volatility and market uncertainty.
One of the most prominent examples of geopolitics’ influence on commodity markets is the impact of political tensions on energy prices. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has disrupted global energy supplies, pushing up prices for oil and natural gas. Similarly, geopolitical events in the Middle East, a major oil-producing region, have often led to price spikes due to concerns about supply disruptions. Geopolitical risks, such as sanctions or embargoes, can also restrict access to key commodities, further influencing market dynamics.
Beyond energy, geopolitics impacts a wide range of commodities. Agricultural markets are susceptible to geopolitical events, as trade restrictions or political instability in major agricultural producers can disrupt global supply chains and drive up prices for grains, coffee, and other agricultural products. The global supply of metals, such as copper and aluminum, is also influenced by geopolitics, as political tensions or resource nationalism can impact production and trade.
For investors navigating the commodity markets, understanding the role of geopolitics is crucial. Geopolitical events can create both opportunities and risks. By closely monitoring global events and understanding their potential impact on commodity markets, investors can make informed decisions and potentially mitigate risks associated with price volatility. Furthermore, investors need to consider the geopolitical implications of their investment decisions, ensuring that they align with their ethical and sustainable investment goals.
Impact of Weather on Agricultural Commodities
Weather plays a crucial role in determining the supply and demand for agricultural commodities. Extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and heat waves can significantly impact crop yields and livestock production, leading to price fluctuations.
Droughts, for example, can cause widespread crop failure, reducing supply and driving up prices. Conversely, excessive rainfall and floods can damage crops and livestock, leading to production losses and price increases.
Temperature fluctuations also have a significant impact. Heat waves can reduce crop yields, while prolonged cold spells can damage fruit trees and other crops. The impact of weather on agriculture is often felt globally, as countries that are major producers of certain commodities experience weather-related production issues.
Investors need to be aware of the impact of weather on agricultural commodities. Understanding the potential for weather-related supply disruptions can help investors make informed decisions about their investments.
For example, investors may choose to invest in agricultural commodities that are less susceptible to weather-related risks or to hedge their investments against potential price fluctuations caused by weather events.
Energy Commodities: Oil, Natural Gas, and More
The energy sector is a vast and complex landscape, driven by the ever-present need for power. At the heart of this sector lie the energy commodities, raw materials that fuel our industries and power our lives. These commodities encompass a wide range of resources, each with its unique characteristics and market dynamics.
Oil, the most prominent energy commodity, remains the lifeblood of the global economy. From transportation to manufacturing, oil underpins countless industries. Its price fluctuates based on factors like supply and demand, geopolitical events, and economic growth.
Natural gas, another crucial energy source, is gaining traction as a cleaner alternative to oil. Its use in electricity generation, heating, and industrial processes is growing rapidly. Natural gas prices are influenced by factors such as weather patterns, production levels, and global demand.
Beyond oil and natural gas, the energy commodity landscape includes a diverse array of resources, including:
- Coal: A traditional fossil fuel, coal remains significant in power generation, particularly in developing economies.
- Uranium: Used in nuclear power plants, uranium is a strategic commodity with a volatile market.
- Renewable energy sources: This category encompasses commodities like solar panels, wind turbines, and biomass, contributing to the transition towards a sustainable energy future.
Understanding the complexities of the energy commodity market is essential for investors seeking to capitalize on its potential. Market forces, geopolitical tensions, technological advancements, and environmental concerns all play a role in shaping the future of these vital resources.
Metals Markets: Gold, Silver, and Industrial Metals
The metals markets, encompassing precious metals like gold and silver and industrial metals such as copper and aluminum, play a significant role in the global economy. These metals are essential components in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, electronics, and jewelry. Understanding the dynamics of these markets is crucial for investors seeking to diversify their portfolios or capitalize on potential price fluctuations.
Gold, often considered a safe-haven asset, tends to perform well during times of economic uncertainty or inflation. Its price is influenced by factors such as geopolitical events, interest rates, and investor sentiment. Silver, another precious metal, has both industrial and investment uses. Its price is tied to both gold and industrial demand.
Industrial metals, including copper, aluminum, and nickel, are crucial for manufacturing and construction. Their prices are heavily influenced by economic growth, supply and demand dynamics, and global trade. For example, copper is a key component in electrical wiring and plumbing, while aluminum finds wide applications in transportation and packaging.
Investors can access the metals markets through various instruments, including exchange-traded funds (ETFs), futures contracts, and physical bullion. ETFs provide a convenient way to gain exposure to a basket of metals, while futures contracts allow investors to speculate on future price movements. Physical bullion offers a tangible asset for portfolio diversification.
The metals markets are dynamic and complex, with numerous factors influencing price movements. It’s essential for investors to carefully research the fundamentals of each metal, understand the risks involved, and develop a sound investment strategy.
Agricultural Commodities: Corn, Wheat, and Soybeans
The agricultural commodity market is a vast and complex ecosystem, with a significant impact on global economies and food security. Corn, wheat, and soybeans are three key players in this market, serving as vital sources of food, feed, and industrial inputs. Understanding the dynamics of these commodities is essential for investors looking to navigate the complexities of this sector.
Corn: The King of Grains
Corn reigns as the world’s most produced grain, playing a crucial role in livestock feed, biofuels, and food production. Factors influencing its price include weather patterns, global demand for animal products, and government policies. For investors, understanding the balance between supply and demand, particularly in major producing regions like the U.S. and Brazil, is key.
Wheat: A Global Staple
Wheat, the backbone of many food systems, experiences price fluctuations driven by factors such as weather conditions, global demand for bread and other wheat-based products, and geopolitical events. Investors should pay attention to production trends in key wheat-producing countries like Russia, the U.S., and Canada, as well as the impact of export policies.
Soybeans: The Versatile Legume
Soybeans are a protein-rich legume used in food, animal feed, and industrial applications. Soybean prices are influenced by factors such as weather conditions, global demand for protein-rich food products, and the use of soybeans in biofuel production. Monitoring production in major soybean-growing areas like the U.S., Brazil, and Argentina is crucial for investors.
The agricultural commodity market, particularly for corn, wheat, and soybeans, presents both opportunities and risks for investors. By understanding the driving forces behind price fluctuations and keeping abreast of global trends, investors can make informed decisions within this vital sector.
Investing in Commodities: ETFs, Futures, and More
Commodities are raw materials that serve as the building blocks for various industries. They range from energy sources like oil and natural gas to precious metals like gold and silver, and agricultural products such as wheat and soybeans. Investing in commodities can diversify your portfolio and offer potential gains, but it’s essential to understand the different ways to participate in this market.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) are a popular way to gain exposure to commodities without directly owning the underlying assets. Commodity ETFs track the performance of specific commodity indices, offering investors a convenient and liquid way to invest in a basket of commodities. Some popular commodity ETFs include the Invesco DB Commodity Index Tracking Fund (DBC) and the United States Oil Fund (USO).
Futures contracts are another way to invest in commodities. They are agreements to buy or sell a specific commodity at a predetermined price on a future date. Futures trading can be more complex than ETFs, requiring a higher level of risk tolerance and trading experience. However, they offer the potential for higher returns and can be used to hedge against price fluctuations.
Beyond ETFs and futures, you can also invest in commodities through other instruments like commodity-linked notes, which are debt securities that pay interest based on the performance of a specific commodity, or commodity-linked mutual funds, which invest in a portfolio of commodity-related assets.
Investing in commodities can be a valuable strategy for portfolio diversification and potential gains. However, it’s crucial to carefully consider your risk tolerance, investment goals, and the specific characteristics of each commodity before making any investment decisions.
Hedging Against Inflation with Commodities
In times of economic uncertainty and rising inflation, investors often turn to commodities as a potential hedge. Commodities, raw materials like oil, gold, and agricultural products, can offer a valuable defense against inflation because their prices tend to rise in line with increasing costs of production and consumer demand.
One key advantage of commodities is their intrinsic value. Unlike stocks or bonds, which represent ownership in a company or debt obligations, commodities are tangible assets with real-world use. When inflation erodes the purchasing power of fiat currency, the value of physical commodities can hold its ground, providing a degree of protection against economic turmoil.
Moreover, commodities can serve as a natural inflation hedge. As inflation spirals upward, the cost of producing goods and services also increases, leading to higher prices for raw materials. This upward pressure on commodity prices can help offset the decline in purchasing power experienced by investors.
However, it’s important to note that investing in commodities comes with risks. Volatility is a prominent feature of the commodity market, and prices can fluctuate significantly due to factors like supply and demand shifts, geopolitical events, and weather patterns. Investors should carefully consider their risk tolerance and investment goals before allocating capital to this asset class.
Despite the risks, commodities can play a role in a diversified investment portfolio by offering a potential hedge against inflation and providing exposure to a different asset class with unique characteristics. As investors navigate the complex landscape of inflation, a thoughtful exploration of the commodity market may offer valuable insights into protecting and growing their wealth.
Risk Management in Commodity Trading
Navigating the world of commodity trading can be both exciting and daunting, offering potential for substantial returns but also presenting significant risks. Risk management is paramount in this realm, as commodities are inherently volatile and subject to various factors, such as weather, global demand, and geopolitical events. A robust risk management strategy can help investors mitigate potential losses and navigate the market with greater confidence.
Here are some key aspects of risk management in commodity trading:
- Diversification: Spreading your investments across different commodities can help reduce the impact of any single commodity’s price fluctuations.
- Hedging: Utilizing financial instruments like futures contracts to offset potential losses from price movements.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Setting predetermined price levels to automatically limit losses on a trade.
- Position Sizing: Carefully determining the amount of capital to allocate to each trade based on risk tolerance and market conditions.
- Thorough Market Research: Staying informed about market trends, fundamental factors influencing commodity prices, and potential risks.
It’s crucial to remember that risk management is an ongoing process. Regular monitoring of your portfolio, adapting your strategy based on market dynamics, and staying disciplined are essential for navigating the complexities of commodity trading effectively.
Analyzing Commodity Market Trends
The commodity market is a dynamic and complex landscape, influenced by a myriad of factors, including supply and demand, global economic conditions, geopolitical events, and technological advancements. Understanding these trends is crucial for investors seeking to navigate this sector effectively.
Supply and Demand Dynamics play a pivotal role in shaping commodity prices. For instance, weather patterns can significantly impact agricultural commodity production, leading to price fluctuations. Similarly, increased demand from emerging economies can drive up prices for industrial metals and energy sources.
Global Economic Conditions also exert a strong influence on commodity markets. Periods of strong economic growth typically lead to higher demand for raw materials, pushing prices upwards. Conversely, economic downturns can dampen demand, causing prices to decline.
Geopolitical Events, such as political instability, trade wars, and natural disasters, can create significant disruptions in commodity markets. These events can impact production, transportation, and consumption patterns, leading to price volatility.
Technological Advancements are also reshaping the commodity landscape. For example, the development of renewable energy sources is impacting the demand for fossil fuels, while advancements in resource extraction and processing technologies are influencing supply dynamics.
Analyzing commodity market trends requires a multi-faceted approach, considering all of these factors in conjunction. Investors need to stay informed about global events, monitor economic indicators, and research technological developments to make informed decisions.
The Future of Commodity Markets
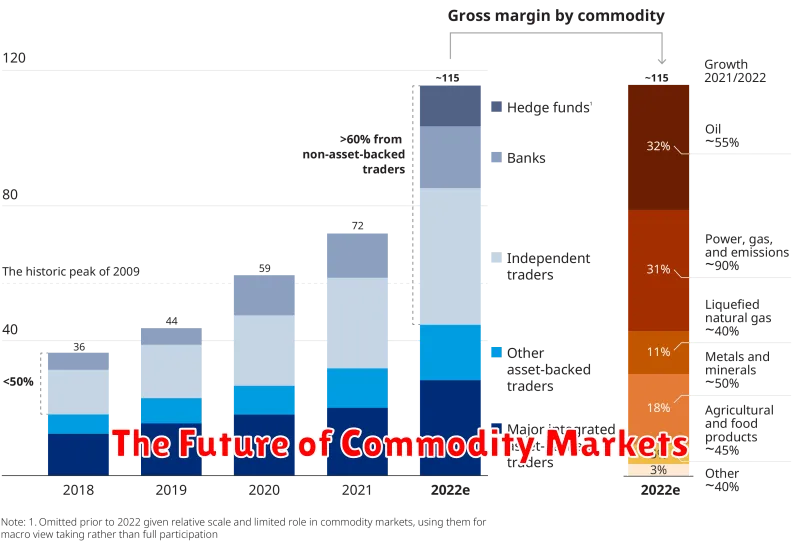
Predicting the future of commodity markets is a complex undertaking, influenced by a multitude of factors including global economic trends, geopolitical events, and technological advancements. However, several key themes are likely to shape the landscape in the coming years.
Sustainability will continue to be a driving force, with increasing demand for environmentally friendly and ethical commodities. This will push producers to adopt sustainable practices and invest in renewable energy sources. Investors are increasingly looking for companies that align with their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) values, influencing the value of commodities.
Technological innovation will play a crucial role in reshaping commodity markets. Automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence are expected to drive efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance transparency in supply chains. The emergence of blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize trade finance, simplify transactions, and improve traceability.
Emerging markets will continue to be a significant driver of commodity demand, particularly in sectors like infrastructure and energy. As developing nations grow and urbanize, the need for raw materials and energy resources will increase, influencing global price dynamics.
Geopolitical risks will continue to be a major factor in commodity market volatility. Trade wars, political instability, and natural disasters can disrupt supply chains and create price shocks. As global tensions rise, understanding geopolitical risks will be essential for successful commodity investments.
The future of commodity markets will be a complex mix of opportunities and challenges. By staying informed about these key themes, investors can navigate the volatility and capitalize on emerging trends. With a focus on sustainability, technological advancements, and a deep understanding of geopolitical risks, investors can position themselves for success in this dynamic market.
Sustainable Investing in Commodities

The commodities market is vast and complex, encompassing everything from oil and gas to agricultural products and precious metals. While traditional commodity investing has often been associated with environmental concerns, a growing trend towards sustainable investing is emerging within this sector. Sustainable commodity investing aims to align investments with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles, ensuring that the production, sourcing, and trading of commodities are conducted in a responsible and ethical manner.
One key aspect of sustainable commodity investing is focusing on renewable energy sources. Investors are increasingly seeking opportunities in commodities like solar and wind energy, which offer a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels. This trend reflects a global shift towards decarbonization and the growing demand for renewable energy solutions.
Another crucial area is responsible sourcing. This involves ensuring that commodities are sourced from suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices, environmental regulations, and responsible land management. For example, investors may choose to invest in agricultural commodities produced sustainably, considering factors like biodiversity conservation, water usage, and soil health.
Furthermore, transparency and accountability are essential in sustainable commodity investing. Companies and investors are increasingly demanding greater transparency in supply chains and the reporting of ESG performance metrics. This includes disclosing information about environmental impacts, social practices, and governance structures.
The emergence of sustainable commodity ETFs and impact investing funds provides investors with access to a growing range of options. These investment vehicles allow investors to allocate their capital towards companies and projects that are actively working to improve the sustainability of the commodities sector.
In conclusion, sustainable investing in commodities presents a compelling opportunity for investors seeking both financial returns and positive social and environmental impact. By focusing on renewable energy, responsible sourcing, transparency, and accountable practices, investors can contribute to a more sustainable future while also benefiting from the potential growth of the commodities market.

