In today’s interconnected world, investors are no longer confined to their domestic markets. The global market presents a vast array of opportunities, offering diversification, growth potential, and access to innovative industries. However, navigating this complex landscape requires a comprehensive understanding of the latest trends, geopolitical factors, and economic indicators. This investor’s guide provides a roadmap to the global market outlook, helping you identify key investment opportunities and mitigate potential risks.
From emerging markets in Asia to established economies in Europe, the world is constantly evolving. Understanding the drivers of economic growth, political stability, and technological advancements is crucial for informed investment decisions. This article explores the key themes shaping the global market landscape, offering insights into investment strategies, sector trends, and risk management. Whether you are a seasoned investor or just starting your journey, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to navigate the global market with confidence.
Understanding the Interconnectedness of Global Markets
The global market is a complex and interconnected web, where events in one part of the world can have a ripple effect on others. Understanding this interconnectedness is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the global landscape. Here are some key factors driving the interconnectedness of global markets:
Trade and Investment Flows: International trade and investment have grown exponentially in recent decades, creating a network of dependencies between countries. This interdependence means that economic shocks in one region can easily spread to others. For example, a slowdown in Chinese demand for commodities can impact commodity prices and the economies of countries that rely on commodity exports.
Global Supply Chains: Modern businesses operate within complex global supply chains, with production processes often spanning multiple countries. Disruptions to these supply chains, such as natural disasters or geopolitical tensions, can have significant impacts on businesses and consumers around the world.
Financial Markets: Capital flows freely across borders, allowing investors to diversify their portfolios and seek out the best returns globally. However, this also means that financial crises in one country can quickly spread to others. For example, the 2008 financial crisis in the United States had a profound impact on global financial markets.
Technology and Innovation: Advances in technology and communication have further integrated global markets, facilitating the exchange of information and goods at unprecedented speed. This can lead to faster diffusion of innovation but also amplifies the impact of economic shocks.
Understanding the interconnectedness of global markets is essential for investors to make informed decisions. By recognizing the potential for contagion, investors can diversify their portfolios across different asset classes and geographic regions to mitigate risk. Moreover, staying informed about global economic trends and political developments is crucial for navigating the complex landscape of the global market.
Key Economic Indicators and their Impact
Understanding the global economic landscape is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the complexities of the market. Key economic indicators provide valuable insights into the health and direction of economies worldwide. These indicators offer a glimpse into factors that influence investment decisions, market trends, and overall economic performance.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a fundamental indicator that measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders. A robust GDP growth rate signifies a healthy economy with strong consumer spending, business investment, and government expenditures. Conversely, a decline in GDP indicates economic contraction and potential recessionary pressures.
Inflation reflects the rate at which prices for goods and services rise over time. Moderate inflation is generally considered healthy for an economy, as it encourages spending and investment. However, high inflation erodes purchasing power and can lead to economic instability. Central banks often use monetary policy tools, such as interest rate adjustments, to manage inflation levels.
Unemployment Rate measures the percentage of the labor force actively seeking employment but unable to find it. A low unemployment rate indicates a strong job market with high levels of economic activity. Conversely, a high unemployment rate suggests weak economic growth and potentially stagnant consumer spending.
Interest Rates play a crucial role in influencing borrowing costs and investment decisions. Central banks manipulate interest rates to control inflation and stimulate economic growth. Lower interest rates encourage borrowing and spending, while higher rates can slow down economic activity but may also attract foreign investment.
Currency Exchange Rates determine the value of one currency relative to another. Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact businesses involved in international trade and investment. A strong currency can make exports more expensive and imports less costly, while a weak currency can boost exports but make imports more expensive.
By closely monitoring these key economic indicators, investors can gain a better understanding of the global economic landscape and make more informed investment decisions. Understanding the relationships between these indicators and their impact on various asset classes is essential for navigating the complexities of the global market.
Geopolitical Factors Influencing Market Trends
The global market is a complex and dynamic system, influenced by a wide range of factors, including geopolitical events. These events can have a significant impact on market trends, investor sentiment, and overall economic growth.
Political Instability and Conflict: Wars, civil unrest, and political transitions can disrupt supply chains, increase commodity prices, and create uncertainty for businesses. These disruptions can lead to market volatility and make it challenging for investors to predict future trends.
Trade Wars and Protectionism: Imposing tariffs and trade restrictions can create barriers to international trade, leading to higher prices for consumers and businesses. These policies can also damage relationships between countries, further impacting market stability.
Geopolitical Alliances and Regional Blocs: The formation or dissolution of alliances and regional blocs can reshape global trade patterns and influence investment flows. These shifts can create opportunities for some countries and industries while posing challenges for others.
Energy Security: Geopolitical events can significantly impact energy markets. Conflicts in energy-producing regions, sanctions, or changes in energy policies can lead to price fluctuations and disrupt the global energy landscape.
Technological Advancements: Geopolitical competition is increasingly playing out in the field of technology. Governments are investing heavily in research and development, seeking to gain an edge in areas such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and cybersecurity. These technological advancements can have far-reaching implications for global markets.
Staying informed about these geopolitical factors is crucial for investors looking to navigate the global market. By understanding the potential impact of these events on different sectors and industries, investors can make more informed decisions and mitigate risks.
Emerging Markets and Investment Opportunities
Emerging markets represent a significant opportunity for investors seeking diversification and potential for higher returns. These markets are characterized by rapid economic growth, rising incomes, and increasing consumer spending. However, navigating these markets can be challenging due to factors like political instability, economic volatility, and regulatory uncertainty. To capitalize on emerging market opportunities, investors must carefully consider the following:
Understanding the Macroeconomic Landscape: A thorough understanding of the macroeconomic environment is crucial. Investors should analyze factors such as GDP growth, inflation, interest rates, and currency exchange rates.
Sector-Specific Opportunities: Emerging markets often offer unique sector-specific investment opportunities. For example, sectors like technology, consumer staples, and healthcare often experience rapid growth in emerging economies.
Risk Management: Emerging markets are inherently more volatile than developed markets. Investors must implement effective risk management strategies, such as diversification and hedging, to mitigate potential losses.
Investment Vehicles: Several investment vehicles can be used to access emerging markets, including mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and direct investments. Each vehicle carries its own risks and rewards, so investors should carefully evaluate their options.
Long-Term Perspective: Investing in emerging markets is a long-term strategy. Investors should not expect quick profits and should be prepared to ride out market fluctuations.
Investing in emerging markets requires careful research, due diligence, and a well-defined investment strategy. By understanding the key factors and opportunities, investors can position themselves to capitalize on the growth potential of these dynamic markets.
Developed Markets and Growth Prospects
Developed markets, characterized by high levels of income, technological advancement, and institutional stability, have historically been a cornerstone of investment portfolios. These markets, which encompass regions like North America, Western Europe, and Japan, offer a range of opportunities for investors seeking stability, consistent returns, and exposure to established companies. However, as the global economic landscape evolves, investors are increasingly evaluating the growth prospects of developed markets in the context of emerging economies and evolving technological trends.
One of the key factors shaping the growth outlook for developed markets is the trend of slowing population growth. As aging populations become the norm in developed countries, consumer spending patterns may shift, potentially leading to slower economic expansion. Furthermore, the increasing adoption of automation and artificial intelligence could lead to job displacement and further complicate the economic outlook.
However, developed markets possess significant advantages that continue to attract investors. Strong institutions, well-developed financial systems, and a skilled workforce provide a solid foundation for economic growth. Moreover, many developed economies are actively pursuing policies aimed at boosting innovation, fostering entrepreneurship, and enhancing productivity. This focus on technological advancements and innovation could create new opportunities for growth and investment.
Investors seeking to capitalize on the growth prospects of developed markets should consider the following factors:
- Sectorial Diversification: Focusing on industries with strong growth potential, such as technology, healthcare, and consumer staples, can enhance returns.
- Value Investing: Seeking undervalued companies with strong fundamentals and a history of profitability can offer attractive investment opportunities.
- Dividend Income: Many established companies in developed markets offer attractive dividend yields, providing a consistent stream of passive income.
In conclusion, developed markets remain an important component of the global investment landscape, offering a balance of stability and growth potential. While challenges such as slowing population growth and technological disruption exist, the strengths of these economies, coupled with ongoing efforts to foster innovation, continue to attract investors seeking long-term value. By carefully evaluating investment opportunities and considering factors such as sectorial diversification and value investing, investors can capitalize on the growth potential of developed markets within their portfolios.
Currency Fluctuations and Exchange Rates
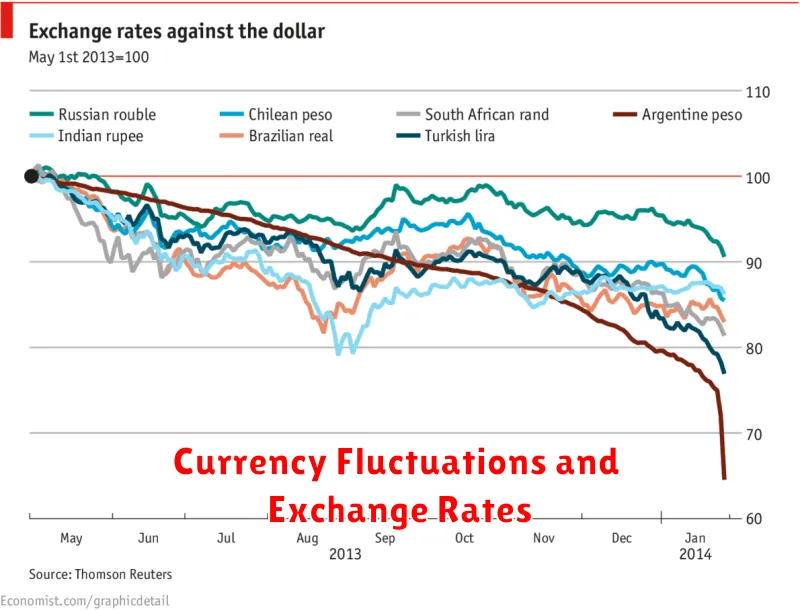
Currency fluctuations are a constant feature of the global marketplace, and understanding their impact is crucial for investors navigating the global landscape. Exchange rates, which determine the value of one currency relative to another, can significantly affect investment returns, especially in international investments. A weakening domestic currency can boost the value of overseas investments when converted back to the domestic currency, while a strengthening domestic currency can have the opposite effect.
Several factors influence currency fluctuations, including:
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth tends to strengthen a currency, as it indicates a healthy economy and higher demand for the currency.
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates can attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the currency and strengthening its value.
- Inflation: High inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, leading to its depreciation.
- Government policies: Fiscal and monetary policies can impact currency values. For example, government intervention in the currency market can influence exchange rates.
- Political stability: Political instability and uncertainty can weaken a currency, as investors may perceive it as a risky investment.
Investors can use various strategies to mitigate the impact of currency fluctuations:
- Diversify investments: Spreading investments across different currencies reduces exposure to the risk of any single currency’s depreciation.
- Use hedging strategies: Hedging involves using financial instruments, such as forward contracts or options, to protect against losses from currency fluctuations.
- Invest in currency-hedged funds: These funds are designed to minimize the impact of currency fluctuations on returns.
Understanding currency fluctuations and their impact on investment returns is essential for investors seeking to navigate the global landscape successfully. By considering the factors that influence exchange rates and employing strategies to manage currency risk, investors can make informed decisions and potentially enhance their investment returns.
Impact of Global Events on Market Sentiment
The global market is a complex and dynamic system, constantly influenced by a multitude of factors. Among these, global events play a pivotal role in shaping market sentiment, impacting investor behavior and asset prices.
Major geopolitical events, such as wars, trade disputes, and political instability, can significantly impact global markets. For example, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine has triggered a surge in commodity prices, particularly for energy and wheat, while also creating uncertainty in global supply chains. This uncertainty can lead to a decline in investor confidence and a shift towards safer assets, like government bonds, causing a dip in stock markets.
Economic developments also exert a powerful influence on market sentiment. A strong economic outlook, characterized by steady growth, low unemployment, and rising consumer spending, typically fosters a positive market mood, attracting investors seeking growth opportunities. Conversely, economic downturns, recessions, and rising inflation can dampen sentiment, leading to market volatility and potentially causing investors to seek safe havens or reduce their risk appetite.
Furthermore, unexpected events, like natural disasters or pandemics, can create significant market disruption. These events can lead to supply chain disruptions, economic uncertainty, and widespread market volatility. The COVID-19 pandemic, for instance, triggered a global recession and triggered drastic market fluctuations, with the early stages of the crisis witnessing sharp sell-offs across asset classes.
Understanding the impact of global events on market sentiment is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the global landscape effectively. By closely monitoring global developments and their potential impact on markets, investors can make informed decisions to mitigate risk, capitalize on opportunities, and enhance their portfolio performance.
Assessing Risk and Volatility in Global Markets

The global market is a complex and ever-changing landscape. Investors face a multitude of risks and uncertainties, making it crucial to carefully assess potential threats and opportunities. This section will explore key factors influencing global market risk and volatility, providing insights into how investors can navigate this dynamic environment.
Geopolitical Risks are a significant source of market uncertainty. These can include international conflicts, trade wars, political instability, and changes in government policies. For example, the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict has significantly impacted global commodity prices and supply chains, creating volatility in energy and agricultural markets.
Economic Risks are another major concern. Factors such as inflation, interest rates, and economic growth prospects can impact market performance. Rising inflation, for instance, can erode purchasing power and lead to higher borrowing costs, potentially slowing economic activity. Central banks’ efforts to control inflation through interest rate hikes can also create volatility, as investors adjust their portfolios in response to changing monetary policy.
Market Volatility is a natural characteristic of financial markets. However, certain factors can exacerbate volatility, such as unexpected events, market sentiment shifts, and investor behavior. The COVID-19 pandemic, for instance, triggered significant market volatility as investors reacted to the uncertainties associated with the health crisis and its economic consequences. This underscores the importance of staying informed about market developments and adjusting investment strategies accordingly.
Assessing and mitigating risks is an ongoing process. Investors can employ various strategies, including diversification, risk management tools, and professional advice, to navigate the complexities of the global market. By understanding the potential risks and opportunities, investors can make informed decisions and pursue their financial goals with greater confidence.
Strategies for Diversifying Globally
Global diversification is a powerful strategy for investors seeking to mitigate risk and enhance returns. It involves allocating investments across different countries and regions, capitalizing on diverse economic trends and market opportunities. Here are some effective strategies for diversifying globally:
1. Invest in International ETFs and Mutual Funds
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and mutual funds provide convenient access to a basket of international stocks and bonds. They offer diversification across various sectors and geographic regions, allowing investors to gain exposure to emerging markets, developed economies, and specific industries.
2. Explore Global Real Estate
Investing in international real estate can provide diversification beyond traditional stock and bond markets. It offers exposure to different property markets, such as residential, commercial, and industrial, and can generate rental income and potential appreciation.
3. Consider Foreign Currency Investments
Currency fluctuations can significantly impact investment returns. Investing in foreign currencies can provide a hedge against currency risk and offer opportunities for growth. Diversifying currency exposure can mitigate losses due to unfavorable exchange rate movements.
4. Leverage Global Private Equity
Private equity investments in international companies can provide access to high-growth opportunities and potential for significant returns. Global private equity firms specialize in identifying and investing in promising companies across various industries and regions.
5. Consult with a Financial Advisor
Seeking professional advice from a financial advisor specializing in international investments can be highly beneficial. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your risk tolerance, investment goals, and financial circumstances, ensuring a well-diversified global portfolio.
By implementing these strategies, investors can navigate the global landscape effectively, reduce risk, and potentially enhance returns. Diversifying globally opens doors to new opportunities and empowers investors to capitalize on the growth potential of the international market.
Investing in International Funds and ETFs
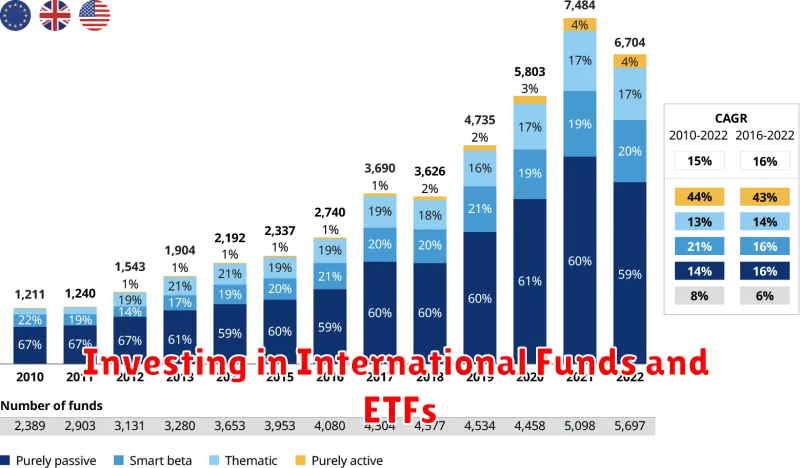
Investing in international funds and ETFs offers a compelling way to diversify your portfolio and gain exposure to the global economy. With a wide range of options available, investors can tap into the growth potential of different countries and sectors around the world.
International funds are actively managed portfolios that invest in securities of companies outside your home country. They offer diversification and professional expertise, but come with higher fees than ETFs.
International ETFs are passively managed funds that track a specific index of international securities. They offer lower costs and transparency, making them an attractive choice for long-term investors.
Before investing in international funds or ETFs, consider the following factors:
- Your investment goals and risk tolerance.
- The specific countries or regions you want to invest in.
- The fund’s expense ratio and performance track record.
- Currency fluctuations and their impact on your returns.
Investing in international funds and ETFs can be a valuable addition to your portfolio, allowing you to participate in the global growth story. However, it’s essential to understand the risks and carefully consider your investment goals before taking the plunge.