Are you looking for a way to make your money work harder for you? Investing in mutual funds can be a great way to achieve your financial goals, whether you’re saving for retirement, buying a house, or just looking to build wealth. But with so many different mutual funds out there, it can be overwhelming to know where to start.
This article will help you navigate the world of mutual funds and explore some of the best mutual funds to invest in. We will discuss different types of mutual funds, the factors to consider when choosing a mutual fund, and provide valuable tips to help you make informed investment decisions. So, if you’re ready to learn how to make your money work for you, keep reading!
Understanding Mutual Funds and their Benefits
Mutual funds are a popular investment vehicle that allows individuals to pool their money together to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities. They are managed by professional fund managers who use their expertise to select and buy a variety of assets, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. Investing in mutual funds offers several benefits, making them a suitable option for both novice and experienced investors.
One of the most significant advantages of mutual funds is diversification. By investing in a mutual fund, you gain exposure to a wide range of assets, reducing the risk associated with investing in individual securities. Diversification helps to spread your investments across different sectors, industries, and asset classes, mitigating the impact of potential losses in any single investment.
Another key benefit is professional management. Mutual funds are managed by experienced fund managers who have the knowledge, resources, and expertise to make informed investment decisions. They continuously monitor market trends, analyze company performance, and adjust the fund’s portfolio to maximize returns while managing risk.
Mutual funds also offer accessibility and affordability. They are available to investors of all income levels, with varying minimum investment requirements. Additionally, they offer flexibility in terms of investment goals and time horizons, allowing you to choose funds that align with your specific needs and risk tolerance.
Moreover, mutual funds provide transparency and accountability. They are required to disclose their holdings and performance regularly, allowing investors to track their investments and make informed decisions. The regulatory framework surrounding mutual funds ensures transparency and ethical practices, protecting investors’ interests.
In conclusion, mutual funds offer several benefits, including diversification, professional management, accessibility, affordability, transparency, and accountability. They provide a convenient and efficient way for individuals to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities, potentially achieving their financial goals while mitigating risk.
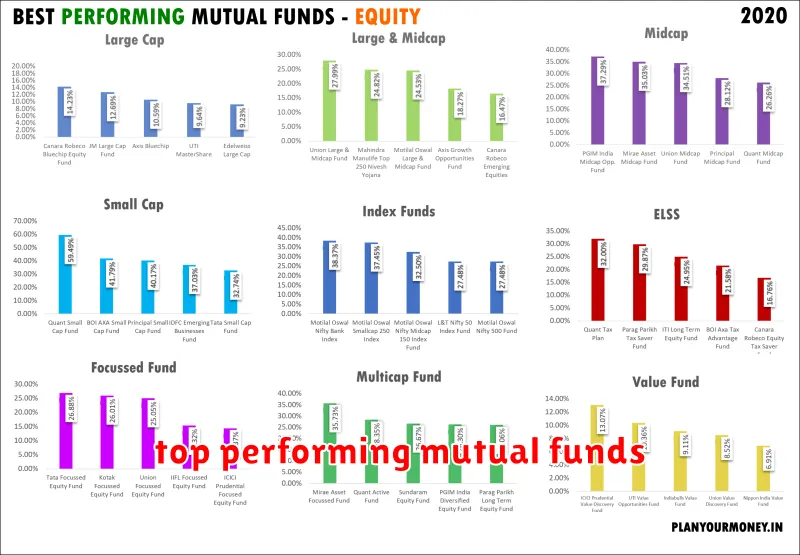
Types of Mutual Funds: Equity, Fixed Income, and More
Mutual funds are a popular investment option, offering diversification and professional management. They pool money from multiple investors to buy a basket of securities, such as stocks, bonds, or other assets. When choosing a mutual fund, understanding the different types is crucial to align your investment goals with the fund’s strategy.
Here’s a breakdown of some common mutual fund categories:
Equity Funds
Equity funds invest primarily in stocks, seeking to generate capital appreciation. They can be further categorized by:
- Large-cap funds: Invest in stocks of large, established companies.
- Mid-cap funds: Focus on companies with a medium market capitalization.
- Small-cap funds: Invest in stocks of smaller, growing companies.
- Growth funds: Seek companies with high growth potential, often in emerging industries.
- Value funds: Look for undervalued companies with strong fundamentals.
- Sector funds: Specialize in specific industries, such as technology, healthcare, or energy.
Fixed Income Funds
Fixed income funds invest in debt securities, such as bonds, which provide a fixed stream of income. They offer lower risk than equity funds but may have lower returns.
- Bond funds: Invest in various types of bonds, including government bonds, corporate bonds, and municipal bonds.
- Money market funds: Invest in short-term debt instruments, providing a safe and liquid investment option.
Other Types of Mutual Funds
Beyond equity and fixed income, other types of mutual funds include:
- Balanced funds: Diversify across stocks and bonds, aiming for both growth and income.
- Index funds: Track a specific market index, like the S&P 500, providing broad market exposure.
- Target-date funds: Adjust their asset allocation based on a specific retirement date, becoming more conservative as the target date approaches.
Selecting the right mutual fund depends on your investment objectives, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Consulting a financial advisor can help you make informed decisions.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Mutual Funds
Investing in mutual funds can be a smart way to diversify your portfolio and achieve your financial goals. However, with so many options available, choosing the right mutual fund can be overwhelming. To help you make an informed decision, here are some crucial factors to consider:
Investment Objective and Risk Tolerance: Before investing, clarify your financial goals and risk appetite. Determine whether you are seeking long-term growth, income generation, or a balanced approach. Consider your tolerance for market fluctuations and select a fund aligned with your objectives.
Fund Manager Expertise and Track Record: The fund manager plays a pivotal role in a mutual fund’s performance. Research the manager’s experience, investment philosophy, and past performance. Look for a consistent track record and a well-defined investment strategy.
Fund Performance and Fees: Analyze the fund’s historical performance, considering factors like average returns, volatility, and risk-adjusted returns. Pay close attention to expense ratios, which represent the annual fees charged for managing the fund. Lower expense ratios generally translate to higher returns for investors.
Fund Size and Liquidity: Larger funds may offer greater diversification and stability. However, consider the fund’s liquidity, which refers to the ease of buying and selling shares. A fund with high liquidity ensures you can access your investment when needed.
Fund Holdings and Sector Exposure: Understand the fund’s portfolio composition and sector exposure. Assess whether the fund aligns with your investment preferences and diversification strategy. Ensure the fund’s holdings are well-diversified across different sectors and asset classes.
Fund Structure and Taxation: Explore the fund’s structure, such as open-ended or closed-ended, and understand its tax implications. Consider factors like dividend payouts and capital gains distributions.
Research and Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research and consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions. Utilize online resources, financial publications, and professional advice to gain a comprehensive understanding of the available options.
Remember, choosing the right mutual fund is an important step in your investment journey. By carefully considering these factors, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Assessing Fund Performance and Track Record
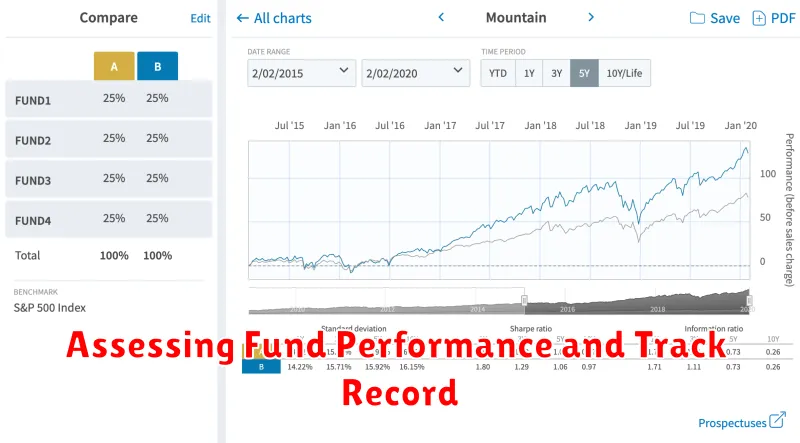
Before investing in any mutual fund, it’s essential to assess its performance and track record. This evaluation process helps you understand how well the fund has performed in the past and provides insights into its potential for future returns. A strong track record doesn’t guarantee future success, but it offers valuable information for your investment decision.
Here are some key metrics to consider when analyzing a fund’s performance:
- Return on Investment (ROI): This metric measures the total profit or loss generated by the fund over a specific period. It’s often expressed as a percentage and helps compare different funds.
- Risk-Adjusted Returns: While high returns are attractive, it’s crucial to consider the associated risk. Metrics like Sharpe Ratio and Treynor Ratio measure how much risk a fund takes to generate its returns. A higher ratio indicates better risk-adjusted performance.
- Consistency: Look for funds that have consistently delivered positive returns over various market conditions. This demonstrates the fund manager’s ability to navigate different economic cycles.
- Benchmark Performance: Compare the fund’s performance against its benchmark index. For example, if a fund invests in large-cap stocks, it should be benchmarked against the S&P 500. Outperforming the benchmark indicates strong fund management.
In addition to performance figures, scrutinize the fund’s management team. Experienced and knowledgeable fund managers with a proven track record often contribute to a fund’s success. Consider factors like their investment philosophy, portfolio construction, and risk management approach.
Remember, past performance is not necessarily indicative of future results. Thorough research and due diligence are essential for making informed investment decisions.
Understanding Expense Ratios and Fees
When it comes to mutual funds, understanding expense ratios and fees is crucial. These costs, though seemingly small, can significantly impact your investment returns over time. Expense ratios are annual fees that cover fund operating expenses, including management fees, administrative costs, and marketing. They are expressed as a percentage of the fund’s assets under management.
For instance, a fund with a 1% expense ratio means that for every $100 you invest, the fund will charge $1 annually to cover its expenses. Fees can be charged when you buy or sell shares in a mutual fund, known as load fees. Loads can be front-end, back-end, or 12b-1 fees.
Front-end loads are charged at the time of purchase, while back-end loads are charged when you sell your shares. 12b-1 fees are used to cover marketing and distribution expenses.
It’s essential to consider the expense ratios and fees when comparing different mutual funds. A lower expense ratio generally means more of your investment goes towards growth, ultimately enhancing your returns. While some investors may believe that higher fees equate to better performance, this isn’t always the case. Look for funds with low expense ratios and reasonable fees to maximize your investment potential.
Active vs. Passive Management: Which is Right for You?
When it comes to investing in mutual funds, you have two primary choices: active management or passive management. Understanding the differences between these approaches is crucial for making informed decisions about your investment strategy.
Active management involves fund managers who actively seek to outperform the market by selecting specific stocks or bonds. They aim to identify undervalued securities and capitalize on market trends, often employing complex strategies and trading frequently.
On the other hand, passive management adopts a more hands-off approach. Passive funds, such as index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs), track a specific market index, like the S&P 500. They aim to mirror the performance of the index, without actively trying to beat it. This approach often involves lower fees and less trading activity.
So, which is right for you? The answer depends on your individual investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Here’s a quick breakdown to help you decide:
Active Management:
- Pros: Potential for higher returns, personalized approach, access to expert management.
- Cons: Higher fees, potential for underperformance, active trading can create tax implications.
Passive Management:
- Pros: Lower fees, typically outperforms active funds over long periods, less volatility.
- Cons: Limited potential for outsized returns, less flexibility in portfolio construction.
Ultimately, the best approach depends on your individual circumstances. If you’re a seasoned investor with a high-risk tolerance and a long-term investment horizon, active management might be a suitable option. However, if you prefer a more hands-off approach with lower costs and consistent returns, passive management could be a better fit.
Diversifying Your Portfolio with Mutual Funds
Mutual funds are a popular investment option for many investors, especially beginners. They offer a way to diversify your portfolio across a wide range of assets, which can help to reduce risk and potentially increase returns. In simple terms, a mutual fund is a collection of stocks, bonds, or other securities that are managed by a professional fund manager. When you invest in a mutual fund, you are essentially buying a small piece of each of the securities in the fund’s portfolio. By doing so, you can gain exposure to a wide range of assets without having to buy each individual security yourself.
One of the biggest advantages of investing in mutual funds is that they provide diversification. Diversification is a key principle of investing that helps to reduce risk. By investing in a variety of different assets, you are less likely to lose all of your money if one particular asset performs poorly. For example, if you invest in a mutual fund that invests in both stocks and bonds, you will be less affected if the stock market takes a downturn. This is because your investment will also be in bonds, which are typically less volatile than stocks.
Another advantage of mutual funds is that they are managed by professionals. When you invest in a mutual fund, you are essentially entrusting your money to a professional fund manager who is responsible for making investment decisions on your behalf. This can be beneficial, especially if you are not experienced in investing or do not have the time to manage your own portfolio.
Of course, no investment is without risk. Mutual funds can be affected by market volatility and economic conditions. However, by carefully choosing a mutual fund and understanding the risks involved, you can help to reduce your risk and potentially achieve your investment goals.
Mutual Funds for Different Investment Goals (Retirement, Education, etc.)

Mutual funds are a popular investment option for a reason: they provide diversification, professional management, and affordability. But how do you choose the right mutual fund for your unique needs? The answer lies in understanding your investment goals.
Retirement: For long-term goals like retirement, consider funds with a long track record of consistent growth. Look for funds with a focus on equity, bonds, or a balanced approach, depending on your risk tolerance and time horizon. Target-date funds are a great option, as they automatically adjust their asset allocation as you get closer to retirement.
Education: Saving for a child’s education is another crucial financial goal. College savings funds are designed specifically for this purpose, often with tax advantages. These funds typically invest in a mix of stocks and bonds, with a higher allocation to stocks during the early years to maximize potential growth.
Short-Term Goals: For shorter-term goals, such as buying a house or a new car, consider funds with a lower risk profile. Money market funds and short-term bond funds are good choices, as they offer stability and potential for modest returns.
It’s crucial to remember that all investments involve risk. Before investing in any mutual fund, be sure to carefully consider your individual circumstances, risk tolerance, and investment goals. Do your research, consult with a financial advisor, and choose funds that align with your financial plan.
Tax Implications of Mutual Fund Investments
Mutual funds, a popular investment vehicle for individuals, offer diversification and professional management. However, understanding the tax implications of mutual fund investments is crucial for maximizing your returns. Here’s a breakdown of the key tax aspects you should be aware of:
Capital Gains Tax: When you sell shares of a mutual fund, you may incur capital gains. These gains are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate if held for a year or less (short-term capital gains) or at preferential rates if held for over a year (long-term capital gains). The tax liability depends on the fund’s holdings and the realized gains or losses.
Dividend Distributions: Mutual funds often distribute dividends earned from underlying investments to their shareholders. These dividends are taxed as ordinary income, and the tax rate varies depending on your income bracket. It’s important to note that dividends are often reinvested back into the fund, further compounding your returns.
Tax-Loss Harvesting: This strategy involves selling losing investments to offset capital gains and reduce your overall tax burden. You can use tax-loss harvesting to offset gains from other investments or to reduce your taxable income.
Tax-Advantaged Accounts: Investing in mutual funds within tax-advantaged accounts like Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or 401(k) plans can offer significant tax benefits. These accounts allow your investments to grow tax-deferred or tax-free, maximizing your long-term returns.
Consult a Financial Advisor: It’s essential to consult with a qualified financial advisor to understand the specific tax implications of your mutual fund investments and develop a comprehensive financial plan that aligns with your goals and risk tolerance. They can help you navigate complex tax rules and make informed decisions to optimize your returns.
Investing in Mutual Funds: Opening an Account and Getting Started

Mutual funds are a popular and accessible investment option for individuals looking to grow their wealth. They offer diversification, professional management, and the potential for long-term returns. But before you can start investing in mutual funds, you need to open an account and understand the basics.
Choosing a Brokerage Account: The first step is to select a brokerage firm that offers mutual funds. Many reputable online brokerages and investment platforms provide access to a wide range of funds. Consider factors like fees, research tools, and customer support when making your choice.
Opening an Account: Once you’ve chosen a brokerage, you’ll need to open an account. This typically involves providing personal information, completing a risk tolerance questionnaire, and funding your account. Ensure you understand the account terms and conditions before proceeding.
Investing in Mutual Funds: With your account funded, you can start investing in mutual funds. You can choose to invest in a lump sum or through regular contributions, known as dollar-cost averaging. Research the funds carefully, considering their investment objective, expense ratio, and performance history.
Important Considerations: It’s crucial to diversify your portfolio across different asset classes and investment styles. Also, remember that mutual funds carry some risk, and their value can fluctuate. Regularly monitor your investments and make adjustments as needed based on your financial goals and risk tolerance.