Are you intrigued by the world of finance and the potential to grow your wealth? Have you ever wondered how to navigate the exciting yet daunting realm of stock trading? Look no further! This comprehensive beginner’s guide, “From Novice to Trader: A Beginner’s Guide on How to Trade Stocks,” is designed to equip you with the essential knowledge and tools to confidently embark on your stock trading journey. Whether you’re a complete newcomer or have some basic understanding, this guide will serve as your roadmap to success.
We’ll demystify the intricacies of stock trading, explaining fundamental concepts like stock markets, buying and selling stocks, different trading strategies, and the importance of risk management. From choosing the right brokerage account to understanding market indicators, we’ll cover everything you need to know to make informed trading decisions. With our step-by-step approach, you’ll gain the confidence to navigate the complexities of the stock market and embark on your path towards financial independence.
What is Stock Trading and How Does it Work?
In essence, stock trading is the buying and selling of shares of publicly listed companies. These shares, also known as stocks, represent ownership in the company. When you buy a stock, you become a part-owner of that company, and you have a claim to its future profits.
The stock market is where these trades occur. There are various stock exchanges worldwide, like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and Nasdaq in the US, and the London Stock Exchange in the UK. These exchanges facilitate the buying and selling of stocks through brokers and electronic trading platforms.
The price of a stock fluctuates based on factors like company performance, market sentiment, and economic conditions. When a company performs well, the demand for its shares increases, driving the price up. Conversely, negative news or poor performance can lead to a decrease in demand and a lower stock price.
Traders buy stocks hoping to sell them at a higher price in the future, making a profit. However, there’s also the risk of losing money if the stock price falls. Understanding the fundamentals of stock trading, such as market analysis, risk management, and investment strategies, is crucial for successful trading.
Setting Up Your Trading Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
Before you can start trading stocks, you’ll need to open a brokerage account. This is where you’ll deposit your money, buy and sell your stocks, and track your investments. Setting up a brokerage account can be surprisingly easy with the right guide. Here’s a step-by-step guide to getting you started.
1. Choose a Brokerage
There are many different brokerages to choose from, each with its own fees, features, and investment options. Here are some things to consider when choosing a brokerage:
- Fees: Brokerage fees can vary widely, so it’s important to compare them before making a decision. Some brokerages charge a commission on every trade, while others offer commission-free trading.
- Features: Some brokerages offer more features than others, such as research tools, charting software, and educational resources.
- Investment Options: Make sure the brokerage you choose offers the types of investments you’re interested in. Some brokerages specialize in stocks, while others offer a wider range of investment options, such as bonds, mutual funds, and ETFs.
2. Provide Personal Information
Once you’ve chosen a brokerage, you’ll need to provide them with some personal information, including your name, address, Social Security number, and date of birth. You’ll also need to provide information about your investment goals and risk tolerance.
3. Fund Your Account
Once your account is set up, you’ll need to fund it with money so you can start trading. Most brokerages offer a variety of funding options, such as bank transfers, wire transfers, and debit card payments.
4. Choose a Trading Platform
Most brokerages offer a variety of trading platforms, both web-based and mobile. These platforms allow you to buy and sell stocks, track your investments, and access research tools. The platform you choose should be user-friendly and have the features you need.
5. Place Your First Trade
You’re now ready to place your first trade. Once you’ve decided on a stock you want to buy, you’ll need to enter the order details, such as the stock symbol, the number of shares, and the order type. You can also set a limit order, which will only execute if the stock price reaches your specified limit.
Ready to Start Trading?
Setting up a brokerage account is just the first step in your trading journey. With a little research and planning, you can set yourself up for success. Remember to always invest wisely and never risk more than you can afford to lose.
Understanding Different Order Types: Market, Limit, Stop-Loss
As a novice trader, understanding different order types is crucial. It’s like knowing the different ways to buy groceries at a supermarket – choosing the right option can significantly impact your trading outcomes. There are primarily three main order types you’ll encounter: market orders, limit orders, and stop-loss orders.
A market order is the simplest and fastest way to execute a trade. It instructs your broker to buy or sell a stock immediately at the best available price in the market. While quick, it doesn’t guarantee the price you’ll get. If the market is volatile, you might end up paying a higher price than expected for buying or selling at a lower price than desired.
A limit order gives you more control over the price. You specify the maximum price you’re willing to pay for buying a stock (limit buy order) or the minimum price you’re willing to accept for selling it (limit sell order). If the market price reaches your limit, your order will be executed. If not, your order will remain pending until the market price reaches your limit or until you cancel it.
A stop-loss order is a risk management tool that helps you limit potential losses. It instructs your broker to sell your stock automatically if the price drops to a certain level (stop-loss price). This is helpful in preventing significant losses in case your stock’s price suddenly drops unexpectedly. It should be set at a reasonable price point below the current market price, based on your risk tolerance.
Fundamental Analysis for Beginners: Evaluating Companies
Fundamental analysis is the process of evaluating a company’s financial performance and overall health. It’s a key part of stock investing, as it helps you understand the underlying value of a company and determine if its stock price is justified. This type of analysis focuses on factors such as revenue, earnings, debt, and management quality.
Financial Statements: The foundation of fundamental analysis is analyzing a company’s financial statements. These documents, including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement, provide a detailed picture of a company’s financial health. By studying these statements, you can identify trends in revenue, profitability, and cash flow.
Key Financial Ratios: Fundamental analysis uses several key financial ratios to evaluate a company’s performance. These ratios can be grouped into categories like profitability, liquidity, solvency, and efficiency. Some common examples include:
- Profitability Ratios: Measure how efficiently a company is using its assets to generate profits (e.g., Return on Equity, Profit Margin).
- Liquidity Ratios: Assess a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations (e.g., Current Ratio, Quick Ratio).
- Solvency Ratios: Show a company’s ability to meet its long-term debt obligations (e.g., Debt-to-Equity Ratio, Times Interest Earned Ratio).
- Efficiency Ratios: Evaluate how effectively a company uses its assets (e.g., Inventory Turnover Ratio, Asset Turnover Ratio).
Industry and Competitive Analysis: It’s crucial to understand the industry in which a company operates and its competitive landscape. Consider factors like industry growth, competitive intensity, and market share. This information helps you assess the company’s potential for future growth and profitability.
Management Quality: The quality of a company’s management team is a crucial aspect of fundamental analysis. Research the management team’s experience, track record, and overall leadership qualities. A strong management team can lead to better decision-making and long-term growth.
Understanding the Big Picture: Fundamental analysis requires looking at the entire picture of a company’s performance. It’s about assessing the company’s past, present, and future prospects. The goal is to identify companies with strong fundamentals, which can translate into future growth and potentially higher stock prices.
Remember, fundamental analysis is an ongoing process. You need to monitor a company’s performance over time and adjust your investment decisions accordingly. The information you gather through fundamental analysis can help you make more informed investment decisions and increase your chances of success in the stock market.
Technical Analysis Basics: Chart Patterns and Indicators
Technical analysis is a method of evaluating securities by analyzing past market data, primarily price and volume. It is used to identify trends and patterns in market behavior, with the goal of predicting future price movements. Technical analysts believe that past price action can provide insights into future price movements, and they use a variety of tools and techniques to analyze charts and identify trading opportunities.
Chart Patterns
Chart patterns are recognizable formations on price charts that can signal potential price movements. Some common chart patterns include:
- Head and Shoulders: A bearish pattern that suggests a reversal of an uptrend.
- Double Top/Bottom: A reversal pattern that indicates a potential change in trend direction.
- Triangles: Consolidation patterns that can signal a breakout in either direction.
- Flags and Pennants: Continuation patterns that suggest a continuation of the current trend.
Indicators
Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on historical price data that can help traders identify trends, momentum, and overbought or oversold conditions. Some popular indicators include:
- Moving Averages: Smoothing out price fluctuations to identify trends.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measuring the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Identifying trend changes and potential reversals.
- Bollinger Bands: Measuring price volatility and identifying potential breakout opportunities.
It’s important to note that technical analysis is not a foolproof method for predicting future market movements. While chart patterns and indicators can provide valuable insights, they should be used in conjunction with other forms of analysis, such as fundamental analysis and risk management strategies. By understanding the basics of technical analysis, traders can improve their decision-making and potentially increase their chances of success in the market.
Managing Risk: Strategies for Protecting Your Investments
Trading stocks can be a lucrative venture, but it also comes with inherent risks. Even the most experienced traders can experience losses, and as a beginner, understanding and managing risk is paramount to your success. This section will delve into some essential strategies for safeguarding your investments.
1. Diversify Your Portfolio: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Diversifying your portfolio across different asset classes, sectors, and industries can help mitigate risk. If one sector performs poorly, others might compensate for the losses.
2. Set Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders are crucial for limiting potential losses. They automatically sell your stocks when they reach a predetermined price, preventing further decline. This helps protect you from significant losses if the market turns against you.
3. Understand Your Risk Tolerance: Before investing, determine your risk tolerance. This refers to your comfort level with potential losses. If you’re risk-averse, stick to more conservative investments. If you’re comfortable with volatility, you can explore riskier assets but remember that higher potential returns often come with higher potential losses.
4. Invest Only What You Can Afford to Lose: Never invest money you cannot afford to lose. Your investments should be a part of your long-term financial plan, and any losses should not impact your everyday life or financial obligations.
5. Research and Due Diligence: Before investing in any stock, conduct thorough research. Understand the company’s financial health, industry trends, and competitive landscape. This will help you make informed decisions and reduce the likelihood of investing in risky or poorly performing companies.
6. Avoid Emotional Trading: Emotions like fear and greed can cloud your judgment. Avoid making impulsive decisions based on short-term market fluctuations. Stick to your investment plan and resist the temptation to panic sell or chase after hot stocks.
7. Learn from Your Mistakes: Every trader makes mistakes. Treat them as learning opportunities. Analyze your trades and identify areas where you can improve your risk management strategies.
By adhering to these strategies, you can significantly reduce your exposure to risk and protect your investments. Remember, managing risk is an ongoing process that requires vigilance and discipline. As you gain experience, you can refine your approach to risk management and become a more confident and successful trader.
Choosing the Right Stocks for Your Portfolio
Choosing the right stocks is crucial for building a successful investment portfolio. You need to carefully consider factors such as your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Fundamental analysis involves examining a company’s financial statements and overall business to understand its strengths and weaknesses. It’s like looking under the hood of a car to see how well it’s built and running.
Technical analysis, on the other hand, focuses on historical price and volume data to identify patterns and trends. This approach is like reading the car’s speedometer and fuel gauge to predict its future movement.
Diversification is another key element to consider. This means investing in a variety of stocks across different sectors and industries. It’s like owning a variety of cars, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, so you’re not overly reliant on any one vehicle.
Value investing involves searching for stocks that are currently undervalued by the market, while growth investing focuses on companies with high growth potential. Think of it as buying a car at a discount or choosing a car that will increase in value over time.
Ultimately, the best stocks for your portfolio will depend on your individual circumstances and preferences. Do your research, consider your goals, and be patient. Building a successful investment portfolio takes time and effort.
The Importance of Patience and Discipline in Trading
Trading stocks can be a thrilling and potentially profitable endeavor, but it’s crucial to approach it with a sound strategy and a mindful mindset. Two of the most vital elements for success are patience and discipline.
Patience allows you to ride out market fluctuations without panicking and making rash decisions. It’s essential to remember that the stock market is inherently volatile and that short-term price movements don’t necessarily reflect a company’s long-term potential. Impatience can lead to hasty buys or sells, potentially resulting in losses.
Discipline is equally important. It involves sticking to your pre-determined trading plan, regardless of emotions or market sentiment. This means setting clear entry and exit points, managing your risk effectively, and avoiding impulsive trades driven by fear or greed.
Here’s how to cultivate patience and discipline in your trading journey:
- Develop a solid trading plan: Define your investment goals, risk tolerance, and preferred trading style.
- Conduct thorough research: Before investing in any company, gain a comprehensive understanding of its financials, industry, and competitive landscape.
- Practice patience: Avoid chasing quick profits. Instead, focus on long-term growth and wait for the right entry and exit points.
- Embrace discipline: Stick to your plan even when the market is volatile. Resist the urge to deviate from your strategy based on emotions.
Remember, trading is a marathon, not a sprint. By prioritizing patience and discipline, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the ups and downs of the market and increase your chances of achieving your financial goals.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make (and How to Avoid Them)
Trading stocks can be a rewarding endeavor, but it’s essential to approach it with a strategy and understanding of common pitfalls. Many beginners make mistakes that can lead to losses, but by being aware of these errors, you can increase your chances of success.
1. Jumping in Without Research: A common mistake is diving into trading without thoroughly researching the company or the market. Before investing in any stock, it’s crucial to understand the company’s financials, its industry, and the overall market trends.
2. Emotional Trading: Let’s face it, emotions can cloud judgment, particularly in the fast-paced world of trading. Panic selling when the market dips or chasing high-flying stocks based on hype can lead to poor decisions. It’s essential to develop a disciplined approach and stick to your trading plan.
3. Overtrading: Many beginners fall into the trap of overtrading, frequently buying and selling stocks without a solid plan. This can lead to higher transaction costs and increase the chances of making impulsive decisions. Focus on a few well-researched stocks and be patient.
4. Ignoring Risk Management: Every investment carries risk, and it’s vital to have a risk management plan in place. This involves setting realistic stop-loss orders, diversifying your portfolio, and avoiding putting all your eggs in one basket. Never invest more than you can afford to lose.
5. Lack of a Trading Plan: A trading plan outlines your investment goals, risk tolerance, and strategy. Without a plan, you’re essentially trading aimlessly. Take the time to develop a well-thought-out trading plan and stick to it, adjusting as needed.
By avoiding these common pitfalls, you can increase your chances of success in the stock market. Remember, trading is a marathon, not a sprint. Focus on learning, developing a sound strategy, and managing your risks to build a solid foundation for long-term growth.
Building a Winning Trading Plan
A trading plan is your roadmap to success in the stock market. It provides structure, discipline, and a clear path to follow, helping you navigate the volatile world of trading.
A well-structured trading plan should encompass several key elements:
- Trading Goals: Define what you hope to achieve through trading. Are you looking for short-term gains, long-term growth, or income generation?
- Risk Tolerance: How much risk are you comfortable taking with your investments? This will determine your trading strategy and asset allocation.
- Trading Strategy: Choose a strategy that aligns with your goals and risk tolerance. Common strategies include day trading, swing trading, and value investing.
- Entry and Exit Points: Determine clear criteria for entering and exiting trades. This might involve using technical indicators, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Set predetermined limits to minimize potential losses. Stop-loss orders automatically sell your position when it reaches a certain price.
- Trade Management: Define rules for managing your open trades, including profit targets, position sizing, and adjustments based on market conditions.
- Record Keeping: Track your trades, analyze your performance, and identify areas for improvement. This is crucial for learning and adapting your plan.
Building a winning trading plan is a continuous process. As your experience and market knowledge grow, you may need to adjust your plan to adapt to changing circumstances. Remember that patience, discipline, and ongoing learning are essential for long-term success in the stock market.
Best Stock Trading Apps for Beginners
Diving into the world of stock trading can feel overwhelming, especially for beginners. Fortunately, the advent of mobile trading apps has made it easier than ever to start investing. These user-friendly platforms offer a simplified interface, educational resources, and often, access to a variety of investment options. Here’s a rundown of some of the best stock trading apps for beginners:
Robinhood
Known for its sleek design and commission-free trades, Robinhood is a popular choice among novice traders. The app boasts a simple, intuitive interface and offers access to a wide range of stocks, ETFs, and options. Robinhood also provides educational content to help users understand the basics of trading. However, it’s essential to remember that the lack of trading fees may not always translate to better returns, and the app’s simplicity can sometimes lack the advanced features needed for more experienced traders.
Webull
Another popular commission-free trading app, Webull stands out with its comprehensive charting tools and research resources. It provides real-time data, market insights, and educational materials to help users make informed trading decisions. Webull also offers fractional shares, allowing beginners to invest in high-priced stocks with smaller amounts of money.
Stash
If you’re new to investing and want to learn as you go, Stash is a great option. It focuses on making investing accessible and affordable, offering fractional shares and a “round-up” feature that automatically invests spare change. Stash also provides personalized learning content and curated investment portfolios based on your goals and risk tolerance.
Acorns
Acorns is a micro-investing app that automatically rounds up your purchases and invests the spare change. It’s a great way to start investing without actively managing your portfolio. Acorns also offers a range of investment options, including ETFs and robo-advisor portfolios.
Ultimately, the best stock trading app for beginners depends on individual preferences and needs. Consider factors like user interface, educational resources, fees, and available investment options before making your decision. Remember that trading involves risk, and it’s crucial to do your research and start small to minimize losses.
Day Trading vs. Swing Trading

Welcome to the world of stock trading! As a beginner, you might be overwhelmed with the different trading styles available. Two popular methods are day trading and swing trading. Understanding their differences will help you decide which one suits your risk tolerance and financial goals.
Day Trading:
Day trading involves buying and selling stocks within a single trading day. Day traders aim to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations, hoping to profit from small price changes. They often use technical analysis tools and rely on high leverage, increasing both potential gains and losses.
Pros of Day Trading:
- Potential for high returns: Fast-paced trading can generate substantial profits if successful.
- Flexibility: Day traders can set their own schedules and work from anywhere with an internet connection.
Cons of Day Trading:
- High risk: Fast-paced trading requires constant attention and involves high risk of losses.
- Time-consuming: Day trading demands a significant commitment of time and energy to monitor market movements.
- High trading costs: Frequent trades can accumulate high commission fees.
Swing Trading:
Swing trading involves holding stocks for a few days to a few weeks, aiming to profit from price swings in a broader market trend. Swing traders focus on identifying short-term trends and capturing price movements within those trends.
Pros of Swing Trading:
- Lower risk: Swing trading holds stocks for a longer period, reducing the risk of short-term fluctuations.
- More relaxed approach: Swing trading requires less constant monitoring than day trading.
- Fewer trading costs: Less frequent trading translates into lower commission fees.
Cons of Swing Trading:
- Lower potential returns: Swing trading’s longer holding periods can limit profit potential compared to day trading.
- Less flexibility: Swing traders need to hold stocks for longer, limiting their ability to react quickly to market changes.
Choosing the Right Trading Style:
The best trading style depends on your personal risk tolerance, financial situation, and available time. If you’re comfortable with high risk and can dedicate significant time, day trading might be suitable. However, if you prefer a more relaxed approach and have limited time, swing trading might be a better option.
Remember, trading involves risks, and you should never invest more than you can afford to lose. It’s crucial to research thoroughly and seek professional advice before embarking on any trading journey.
How to Read Stock Charts
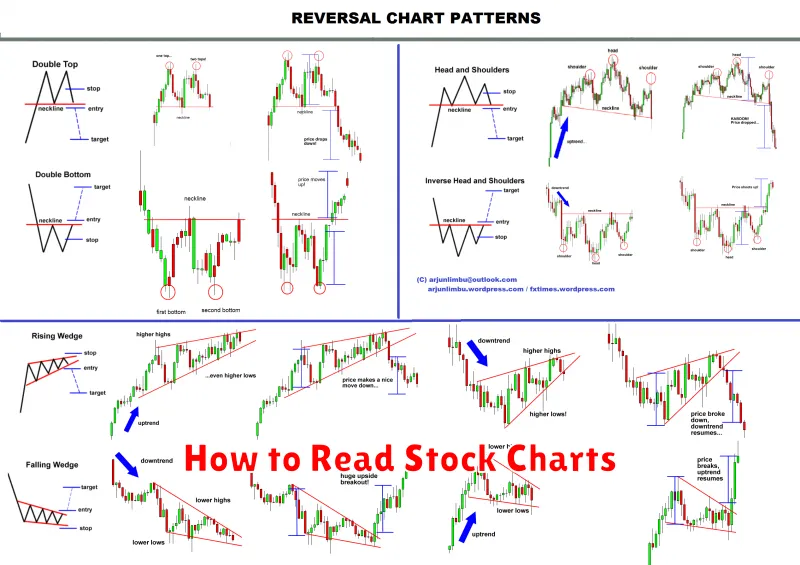
Stock charts are the language of the stock market. They provide a visual representation of a stock’s price movements over time, offering valuable insights into its historical performance and potential future trends. Learning to read stock charts is essential for any trader, regardless of experience level.
The most common type of stock chart is the line chart, which simply connects the closing prices of a stock over a period of time. A candlestick chart provides more detailed information by showing the open, high, low, and closing prices for each trading period.
When interpreting stock charts, look for key patterns that can signal potential buying or selling opportunities. Uptrends are characterized by a series of higher highs and higher lows, while downtrends show lower highs and lower lows. Support and resistance levels are price points where the stock tends to find support or resistance.
Technical indicators are also valuable tools for analyzing stock charts. Moving averages, for example, can help smooth out price fluctuations and identify trends. Relative strength index (RSI) is a momentum indicator that can help detect overbought or oversold conditions.
Remember that stock charts are just one piece of the puzzle when making trading decisions. It’s important to consider other factors such as company fundamentals, market sentiment, and economic conditions. However, mastering the art of reading stock charts can provide a significant advantage in navigating the volatile world of trading.
Understanding Stock Market Volatility
The stock market is a dynamic environment where prices constantly fluctuate. This fluctuation is known as volatility, and it’s a crucial factor for investors to understand. Volatility reflects the rate and magnitude of price changes, influencing the risk and potential reward of investments.
High volatility means prices are changing rapidly and significantly. This can be caused by various factors, including:
- Economic news: Unexpected economic data, such as inflation reports or interest rate changes, can trigger market swings.
- Political events: Geopolitical tensions, elections, or policy changes can impact investor sentiment and lead to volatility.
- Company-specific news: Earnings reports, mergers, or product launches can affect individual company stock prices.
Low volatility indicates stable prices with minimal fluctuations. This can occur during periods of economic stability and investor confidence.
Understanding volatility is essential for traders and investors as it helps them:
- Assess risk: High volatility implies greater risk, as prices can move sharply against your position.
- Develop trading strategies: Different volatility levels call for different trading approaches. High volatility might favor short-term trading, while low volatility could suit long-term investments.
- Manage expectations: Volatility is a natural part of the market. Being prepared for price swings helps you avoid impulsive decisions.
While volatility can be unsettling, it’s important to remember that it’s not necessarily a bad thing. It creates opportunities for both buying and selling. Learning to understand and navigate volatility is crucial for success in the stock market.
Importance of a Trading Journal

In the realm of stock trading, a trading journal is an indispensable tool that can significantly enhance your journey from novice to experienced trader. It serves as a comprehensive record of your trading activities, providing invaluable insights into your strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
One of the primary benefits of a trading journal is its ability to foster self-awareness. By documenting your trades, you gain a deeper understanding of your trading patterns, biases, and emotional responses to market fluctuations. This introspection allows you to identify and address any detrimental habits that may be hindering your profitability.
Furthermore, a trading journal facilitates performance analysis. By tracking your trades, you can evaluate your win-loss ratio, average profit/loss per trade, and overall performance metrics. This data enables you to assess the effectiveness of your trading strategies and make informed adjustments to optimize your approach.
Moreover, a trading journal serves as a valuable learning tool. It allows you to review past trades and identify the factors that contributed to your successes and failures. By analyzing your mistakes, you can learn from them and avoid repeating them in the future. This iterative process of learning and improvement is crucial for long-term success in the markets.
In conclusion, maintaining a trading journal is essential for any aspiring trader. It empowers you with self-awareness, performance analysis, and valuable learning experiences. By embracing this practice, you lay the foundation for a more disciplined, profitable, and fulfilling trading journey.

